Occurrence of Invasive Pulmonary Fungal Infections in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Admitted to the ICU
- PMID: 33480831
- PMCID: PMC7874326
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202009-3400OC
Occurrence of Invasive Pulmonary Fungal Infections in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Admitted to the ICU
Abstract
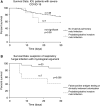
Rationale: Whether severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a significant risk factor for the development of invasive fungal superinfections is of great medical interest and remains, for now, an open question.Objectives: We aim to assess the occurrence of invasive fungal respiratory superinfections in patients with severe COVID-19.Methods: We conducted the study on patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-related pneumonia admitted to five ICUs in France who had respiratory and serum sampling performed for specific screening of fungal complications.Measurements and Main Results: The study population included a total of 145 patients; the median age was 55 years old. Most of them were male (n = 104; 72%), were overweight (n = 99; 68%), and had hypertension (n = 83; 57%) and diabetes (n = 46; 32%). Few patients presented preexisting host risk factors for invasive fungal infection (n = 20; 14%). Their global severity was high; all patients were on invasive mechanical ventilation, and half (n = 73, 54%) were on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. Mycological analysis included 2,815 mycological tests (culture, galactomannan, β-glucan, and PCR) performed on 475 respiratory samples and 532 sera. A probable/putative invasive pulmonary mold infection was diagnosed in 7 (4.8%) patients and linked to high mortality. Multivariate analysis indicates a significantly higher risk for solid organ transplant recipients (odds ratio, = 4.66; interquartile range, 1.98-7.34; P = 0.004). False-positive fungal test and clinically irrelevant colonization, which did not require the initiation of antifungal treatment, was observed in 25 patients (17.2%).Conclusions: In patients with no underlying immunosuppression, severe SARS-CoV-2-related pneumonia seems at low risk of invasive fungal secondary infection, especially aspergillosis.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; aspergillosis; aspergillus; fungal infection.
Figures
Comment in
-
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Goes Viral Again?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Feb 1;203(3):275-277. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202012-4413ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33352060 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA. 2020;323:1775–1776. [Published erratum appears in JAMA 323:1619.] - PubMed
-
- D’Antiga L. Coronaviruses and immunosuppressed patients: the facts during the third epidemic. Liver Transpl. 2020;26:832–834. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

