MicroRNA-374b inhibits breast cancer progression through regulating CCND1 and TGFA genes
- PMID: 33480984
- PMCID: PMC8086770
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgab005
MicroRNA-374b inhibits breast cancer progression through regulating CCND1 and TGFA genes
Abstract
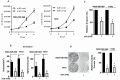
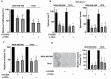
Emerging evidence indicates that microRNAs (miRNAs) play a critical role in breast cancer development. We recently reported that a higher expression of miR-374b in tumor tissues was associated with a better disease-free survival of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). However, the functional significance and molecular mechanisms underlying the role of miR-374b in breast cancer are largely unknown. In this current study, we evaluated the biological functions and potential mechanisms of miR-374b in both TNBC and non-TNBC. We found that miR-374b was significantly downregulated in breast cancer tissues, compared to adjacent tissues. MiR-374b levels were also lower in breast cancer cell lines, as compared to breast epithelial cells. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that miR-374b modulates the malignant behavior of breast cancer cells, such as cell proliferation in 2D and 3D, cell invasion ability, colony-forming ability and tumor growth in mice. By using bioinformatics tools, we predicted that miR-374b plays a role in breast cancer cells through negatively regulating cyclin D1 (CCND1) and transforming growth factor alpha (TGFA). We further confirmed that CCND1 and TGFA contribute to the malignant behavior of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Our rescue experiments showed that overexpressing CCND1 or TGFA reverses the phenotypes caused by miR-374b overexpression. Taken together, our studies suggest that miR-374b modulates malignant behavior of breast cancer cells by negatively regulating CCND1 and TGFA genes. The newly identified miR-374b-mediated CCND1 and TGFA gene silencing may facilitate a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of breast cancer progression.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Brennecke, J., et al. (2003) bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell, 113, 25–36. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C.Z., et al. (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science, 303, 83–86. - PubMed
-
- Schratt, G.M., et al. (2006) A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature, 439, 283–289. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

