Renal function in a cohort of HIV-infected patients initiating antiretroviral therapy in an outpatient setting in Ethiopia
- PMID: 33481839
- PMCID: PMC7822244
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245500
Renal function in a cohort of HIV-infected patients initiating antiretroviral therapy in an outpatient setting in Ethiopia
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the prevalence and associated factors of abnormal renal function among Ethiopian HIV-infected patients at baseline prior to initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and during follow-up.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational cohort study of HIV infected patients who initiated ART at the outpatient ART clinic of Mehal Meda Hospital of North Shewa, Ethiopia from January 2012 to August 2018. Demographic and clinical data were abstracted from the medical records of patients. Renal function was assessed by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) calculated using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation. Univariate and multivariate analysis were conducted to determine the factors associated with abnormal renal function at baseline and during follow-up.
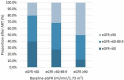
Results: Among 353 patients, 70 (19.8%) had baseline eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73m2 and 102 (28.9%) had eGFR = 60-89.9 ml/min/1.73m2. Factors associated with baseline renal impairment (eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73m2) included female sex (AOR = 3.52, CI 1.75-7.09), CD4 count < 200 cells/mm3 (AOR = 2.75, CI 1.40-5.42), BMI < 25 Kg/m2 (AOR = 3.04, CI 1.15-8.92), low hemoglobin (AOR = 2.19, CI 1.16-4.09) and high total cholesterol (AOR = 3.15, CI 1.68-5.92). After a median of 3.0 years of ART, the mean eGFR declined from 112.9 ± 81.2 ml/min/1.73m2 at baseline to 93.9 ± 60.6 ml/min/1.73m2 (P < 0.001). The prevalence of renal impairment increased from 19.8% at baseline to 22.1% during follow-up. Of 181 patients with baseline normal renal function, 49.7% experienced some degree of renal impairment. Older age (AOR = 3.85, 95% CI 2.03-7.31), female sex (AOR = 4.18, 95% CI 2.08-8.40), low baseline CD4 (AOR = 2.41, 95% CI 1.24-4.69), low current CD4 count (AOR = 2.32, 95% CI 1.15-4.68), high BMI (AOR = 2.91, 95% CI 1.49-5.71), and low hemoglobin (AOR = 3.38, 95% CI 2.00-7.46) were the factors associated with renal impairment during follow-up.
Conclusion: Impaired renal function was common in HIV-infected patients initiating ART in an outpatient setting in Ethiopia, and there appears to be a high prevalence of renal impairment after a median ART follow-up of 3 years. There is a need for assessment of renal function at baseline before ART initiation and regular monitoring of renal function for patients with HIV during follow-up.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of dyslipidaemia among HIV-infected patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy in North Shewa, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 27;16(4):e0250328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250328. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33905435 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Function in Chinese HIV-Positive Individuals following Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0135462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135462. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317657 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the universal test and treat strategy on the kidney function in adults living with HIV in Zambia: A six-month multicenter cohort study.PLoS One. 2025 May 12;20(5):e0323618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323618. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40354477 Free PMC article.
-
Renal manifestations of HIV during the antiretroviral era in South Africa: a systematic scoping review.Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 13;6(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s13643-017-0605-5. Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29029647 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Profile of People Living with HIV in a Treatment Hub in Manila, Philippines: A Pre- and Post-Antiretroviral Analysis.J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2022;37(1):53-61. doi: 10.15605/jafes.037.01.17. Epub 2022 Feb 18. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2022. PMID: 35800599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Incidence, progression and predictors of chronic kidney disease among adult HIV/AIDS patients on antiretroviral treatment in comprehensive specialised hospitals in the Amhara Region, Ethiopia, 2022: a multi-centre retrospective follow-up study.BMJ Open. 2025 Jul 8;15(7):e090345. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-090345. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40633949 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury and its predictors among HIV-positive patients in Africa: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 9;19(2):e0298302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298302. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38335171 Free PMC article.
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus-positive Patients on Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Continue to Have a Decline in Renal Function Irrespective of Tenofovir Usage.J Glob Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 27;16(3):111-116. doi: 10.4103/jgid.jgid_125_23. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. J Glob Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39619365 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of chronic kidney disease among young people living with HIV in Sub Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 4;19(11):e0301954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301954. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39495780 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and associated factors of chronic kidney disease among adults receiving antiretroviral therapy at Hawassa University Comprehensive Specialized Hospital.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 3;20(4):e0320787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320787. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40179103 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous