Water quality assessment and source identification of the Shuangji River (China) using multivariate statistical methods
- PMID: 33481880
- PMCID: PMC7822302
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245525
Water quality assessment and source identification of the Shuangji River (China) using multivariate statistical methods
Abstract
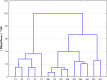
Multivariate statistical techniques, including cluster analysis (CA), discriminant analysis (DA), principal component analysis (PCA) and factor analysis (FA), were used to evaluate temporal and spatial variations in and to interpret large and complex water quality datasets collected from the Shuangji River Basin. The datasets, which contained 19 parameters, were generated during the 2 year (2018-2020) monitoring programme at 14 different sites (3192 observations) along the river. Hierarchical CA was used to divide the twelve months into three periods and the fourteen sampling sites into three groups. Discriminant analysis identified four parameters (CODMn, Cu, As, Se) loading more than 68% correct assignations in temporal analysis, while seven parameters (COD, TP, CODMn, F, LAS, Cu and Cd) to load 93% correct assignations in spatial analysis. The FA/PCA identified six factors that were responsible for explaining the data structure of 68% of the total variance of the dataset, allowing grouping of selected parameters based on common characteristics and assessing the incidence of overall change in each group. This study proposes the necessity and practicality of multivariate statistical techniques for evaluating and interpreting large and complex data sets, with a view to obtaining better information about water quality and the design of monitoring networks to effectively manage water resources.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)--a case study.Water Res. 2004 Nov;38(18):3980-92. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011. Water Res. 2004. PMID: 15380988
-
Use of multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of temporal and spatial variations in water quality of the Kaduna River, Nigeria.Environ Monit Assess. 2015 Mar;187(3):137. doi: 10.1007/s10661-015-4354-4. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Environ Monit Assess. 2015. PMID: 25707603
-
Integrated Application of Multivariate Statistical Methods to Source Apportionment of Watercourses in the Liao River Basin, Northeast China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Oct 21;13(10):1035. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13101035. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27775679 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: case study of the Nampong River and Songkhram River, Thailand.Environ Monit Assess. 2015 Sep;187(9):548. doi: 10.1007/s10661-015-4774-1. Epub 2015 Aug 2. Environ Monit Assess. 2015. PMID: 26233666
-
Temporal and spatial assessment of river surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a study in Can Tho City, a Mekong Delta area, Vietnam.Environ Monit Assess. 2015 May;187(5):229. doi: 10.1007/s10661-015-4474-x. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Environ Monit Assess. 2015. PMID: 25847419
Cited by
-
Multivariate analyses of water quality indices and incidence of Aeromonas species in water from different holding facilities in Kwara State, Nigeria.BMC Vet Res. 2025 May 28;21(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04830-9. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40426175 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Water Quality Patterns in an Estuarine Reservoir and the Functional Changes in Relations of Trophic State Variables Depending on the Construction of Serial Weirs in Upstream Reaches.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 29;18(23):12568. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182312568. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34886296 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Multivariate Statistical Techniques and Water Quality Index for the Assessment of Water Quality and Apportionment of Pollution Sources in the Yeongsan River, South Korea.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 4;18(16):8268. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168268. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34444013 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of imbalances in essential/toxic metal levels in the blood of laryngeal cancer patients in comparison with controls.Biometals. 2023 Feb;36(1):111-127. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00464-8. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 36370262
References
-
- Nowak B, Nadolna A, Stanek P. Evaluation of the potential for the use of lakes in restoring water resources and flood protection, with the example of the Noteć Zachodnia River catchment (Gniezno Lakeland, Poland). Meteorology Hydrology and Water Management. 2018. 2018-05-14.
-
- Twine TE, Kucharik CJ, Foley JA. Effects of El Niño–Southern Oscillation on the Climate, Water Balance, and Streamflow of the Mississippi River Basin. J CLIMATE. 2005. 2005-11-15;18(22):4840–61.
-
- Younis AM, Ismail IS, Mohamedein L, Ahmed SF. Spatial Variation and Environmental Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in the Surficial Sediments along the Egyptian Red Sea Coast. Catrina: The International Journal of Environmental Sciences. 2015;10(1):45–52.
-
- Younis AM, Ismail IS, Mohamedein L, Ahmed SF. Spatial Variation and Environmental Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in the Surficial Sediments along the Egyptian Red Sea Coast. Catrina: The International Journal of Environmental Sciences. 2015;10(1):45–52.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

