The magnitude of COVID-19's effect on the timely management of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers
- PMID: 33482258
- PMCID: PMC7817517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.12.065
The magnitude of COVID-19's effect on the timely management of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers
Keywords: COVID-19; basal cell carcinoma; cutaneous melanoma; cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; diagnostic delay; nonmelanoma skin cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest None disclosed.
Figures
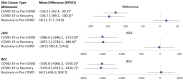
Similar articles
-
Cutaneous malignancies: melanoma and nonmelanoma types.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011 Mar;127(3):37e-56e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318206352b. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011. PMID: 21364382 Review.
-
Diagnostic Delays for Non-melanoma Skin Cancers in Renal Transplant Recipients during the COVID-19 Pandemic: What is Hiding Behind the Mask?Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021 Jul;29(2):111-113. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021. PMID: 34477079
-
Common skin cancers in older adults: approach to diagnosis and management.Clin Geriatr Med. 2013 May;29(2):361-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2013.01.011. Clin Geriatr Med. 2013. PMID: 23571033 Review.
-
Duration of acceptable delay between the time of diagnosis and treatment of melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022 Jun;36(6):e460-e464. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17950. Epub 2022 Feb 3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022. PMID: 35067989 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diagnosis and management of skin cancer.Cancer. 1983 Jun 15;51(12 Suppl):2448-52. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830615)51:12+<2448::aid-cncr2820511311>3.0.co;2-l. Cancer. 1983. PMID: 6850522
Cited by
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on skin cancer incidence and treatment in England, 2020.Br J Dermatol. 2021 Aug;185(2):460-462. doi: 10.1111/bjd.20409. Epub 2021 May 31. Br J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33937975 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Health Economic Consequences Associated With COVID-19-Related Delay in Melanoma Diagnosis in Europe.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Feb 5;7(2):e2356479. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.56479. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38363565 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Covid-19 on the management of patients with metastatic melanoma.Oncotarget. 2022 Dec 29;13:1370-1379. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28333. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 36580495 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on melanoma diagnosis.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021 Nov;35(11):e714-e715. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17493. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021. PMID: 34236721 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reduction in the number of early melanomas diagnosed during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-centre cohort study.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021 Nov;35(11):e735-e737. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17522. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021. PMID: 34260770 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- COVID-19 resources. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. https://www.nccn.org/covid-19/ Accessed September 25, 2020. Available at:
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

