The Ubiquitin E3 Ligase TRIM21 Promotes Hepatocarcinogenesis by Suppressing the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant Pathway
- PMID: 33482392
- PMCID: PMC8024979
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.01.007
The Ubiquitin E3 Ligase TRIM21 Promotes Hepatocarcinogenesis by Suppressing the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant Pathway
Abstract
Background and aims: TRIM21 is a ubiquitin E3 ligase that is implicated in numerous biological processes including immune response, cell metabolism, redox homeostasis, and cancer development. We recently reported that TRIM21 can negatively regulate the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 antioxidant pathway by ubiquitylating p62 and prevents its oligomerization and protein sequestration function. As redox homeostasis plays a pivotal role in many cancers including liver cancer, we sought to determine the role of TRIM21 in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Methods: We examined the correlation between TRIM21 expression and the disease using publicly available data sets and 49 cases of HCC clinical samples. We used TRIM21 genetic knockout mice to determine how TRIM21 ablation impact HCC induced by the carcinogen DEN plus phenobarbital (PB). We explored the mechanism that loss of TRIM21 protects cells from DEN-induced oxidative damage and cell death.
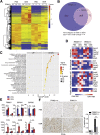
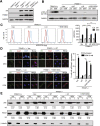
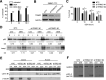
Results: There is a positive correlation between TRIM21 expression and HCC. Consistently, TRIM21-knockout mice are resistant to DEN-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. This is accompanied by decreased cell death and tissue damage upon DEN treatment, hence reduced hepatic tissue repair response and compensatory proliferation. Cells deficient in TRIM21 display enhanced p62 sequestration of Keap1 and are protected from DEN-induced ROS induction and cell death. Reconstitution of wild-type but not the E3 ligase-dead and the p62 binding-deficient mutant TRIM21 impedes the protection from DEN-induced oxidative damage and cell death in TRIM21-deficient cells.
Conclusions: Increased TRIM21 expression is associated with human HCC. Genetic ablation of TRIM21 leads to protection against oxidative hepatic damage and decreased hepatocarcinogenesis, suggesting TRIM21 as a preventive and therapeutic target.
Keywords: Diethylnitrosamine; Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Nrf2; TRIM21; p62.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus NSs Interacts with TRIM21 To Activate the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway.J Virol. 2020 Feb 28;94(6):e01684-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01684-19. Print 2020 Feb 28. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31852783 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM21 Ubiquitylates SQSTM1/p62 and Suppresses Protein Sequestration to Regulate Redox Homeostasis.Mol Cell. 2016 Mar 3;61(5):720-733. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.007. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26942676 Free PMC article.
-
GSTZ1 deficiency promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via activation of the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 30;38(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1459-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31666108 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induction by Aberrant NRF2 Activation-Mediated Transcription Networks: Interaction of NRF2-KEAP1 Controls the Fate of Hepatocarcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5378. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155378. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular mechanisms that drive intracellular neutralization by the antibody-receptor and RING E3 ligase TRIM21.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun;126:99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 34823983 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of the Prognostic Values of the TRIM Family in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 23;11:767644. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.767644. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35004288 Free PMC article.
-
CLEC-1 is a death sensor that limits antigen cross-presentation by dendritic cells and represents a target for cancer immunotherapy.Sci Adv. 2022 Nov 16;8(46):eabo7621. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo7621. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36399563 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic TGM2 promotes malignant progression in gastric cancer by suppressing the TRIM21-mediated ubiquitination/degradation of STAT1 in a GTP binding-dependent modality.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023 Jan;43(1):123-149. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12386. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36353796 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM21-Promoted FSP1 Plasma Membrane Translocation Confers Ferroptosis Resistance in Human Cancers.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Oct;10(29):e2302318. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302318. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37587773 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 targets TIF1γ to regulate β-catenin signaling in glioblastoma.Theranostics. 2023 Sep 4;13(14):4919-4935. doi: 10.7150/thno.85662. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37771771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choi J. Oxidative stress, endogenous antioxidants, alcohol, and hepatitis C: pathogenic interactions and therapeutic considerations. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52:1135–1150. - PubMed
-
- Gambino R., Musso G., Cassader M. Redox balance in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15:1325–1365. - PubMed
-
- Komatsu M., Kurokawa H., Waguri S., Taguchi K., Kobayashi A., Ichimura Y., Sou Y.S., Ueno I., Sakamoto A., Tong K.I., Kim M., Nishito Y., Iemura S., Natsume T., Ueno T., Kominami E., Motohashi H., Tanaka K., Yamamoto M. The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:213–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

