Brewers' spent grain as substrate for dextran biosynthesis by Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides DSM20193 and Weissella confusa A16
- PMID: 33482833
- PMCID: PMC7821685
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-021-01515-4
Brewers' spent grain as substrate for dextran biosynthesis by Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides DSM20193 and Weissella confusa A16
Abstract
Background: Lactic acid bacteria can synthesize dextran and oligosaccharides with different functionality, depending on the strain and fermentation conditions. As natural structure-forming agent, dextran has proven useful as food additive, improving the properties of several raw materials with poor technological quality, such as cereal by-products, fiber-and protein-rich matrices, enabling their use in food applications. In this study, we assessed dextran biosynthesis in situ during fermentation of brewers´ spent grain (BSG), the main by-product of beer brewing industry, with Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides DSM20193 and Weissella confusa A16. The starters performance and the primary metabolites formed during 24 h of fermentation with and without 4% sucrose (w/w) were followed.
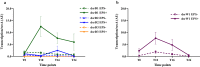
Results: The starters showed similar growth and acidification kinetics, but different sugar utilization, especially in presence of sucrose. Viscosity increase in fermented BSG containing sucrose occurred first after 10 h, and it kept increasing until 24 h concomitantly with dextran formation. Dextran content after 24 h was approximately 1% on the total weight of the BSG. Oligosaccharides with different degree of polymerization were formed together with dextran from 10 to 24 h. Three dextransucrase genes were identified in L. pseudomesenteroides DSM20193, one of which was significantly upregulated and remained active throughout the fermentation time. One dextransucrase gene was identified in W. confusa A16 also showing a typical induction profile, with highest upregulation at 10 h.
Conclusions: Selected lactic acid bacteria starters produced significant amount of dextran in brewers' spent grain while forming oligosaccharides with different degree of polymerization. Putative dextransucrase genes identified in the starters showed a typical induction profile. Formation of dextran and oligosaccharides in BSG during lactic acid bacteria fermentation can be tailored to achieve specific technological properties of this raw material, contributing to its reintegration into the food chain.
Keywords: Brewers’ spent grain; Dextran; Fermentation; Lactic acid bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Mussatto SI, Dragone G, Roberto IC. Brewers’ spent grain: generation, characteristics and potential applications. J Cereal Sci. 2006;43:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2005.06.001. - DOI
-
- Lynch KM, Steffen EJ, Arendt EK. Brewers’ spent grain: a review with an emphasis on food and health. J Inst Brew. 2016;122:553–68. doi: 10.1002/jib.363. - DOI
-
- Öztürk S, Özboy Ö, Cavidoǧlu I, Köksel H. Effects of brewer’s spent grain on the quality and dietary fibre content of cookies. J Inst Brew. 2002;108:23–27. doi: 10.1002/j.2050-0416.2002.tb00116.x. - DOI
-
- Waters DM, Jacob F, Titze J, Arendt EK, Zannini E. Fibre, protein and mineral fortification of wheat bread through milled and fermented brewer’s spent grain enrichment. Eur Food Res Technol. 2012;235:767–778. doi: 10.1007/s00217-012-1805-9. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

