Experimental evaluation of direct thromboaspiration efficacy according to the angle of interaction between the aspiration catheter and the clot
- PMID: 33483456
- PMCID: PMC8606460
- DOI: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016889
Experimental evaluation of direct thromboaspiration efficacy according to the angle of interaction between the aspiration catheter and the clot
Abstract
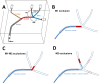
Background: Successful direct thromboaspiration (DTA) is related to several factors such as clot consistency, size, and location. It has also been demonstrated recently that the angle of interaction (AOI) formed by the aspiration catheter and the clot is related to DTA efficacy. The aims of this study were three-fold: (a) to confirm the clinical finding that the AOI formed by the aspiration catheter and the clot influence DTA efficacy; (b) to evaluate to what extent this influence varies according to differences in clot consistency and size; and (c) to validate stent retriever thrombectomy as an effective rescue treatment after DTA failure in the presence of an unfavorable AOI.
Methods: A rigid vascular phantom designed to reproduce a middle cerebral artery trifurcation anatomy with three M2 segments forming different angles with M1 and thrombus analog of different consistencies and sizes was used.
Results: DTA was highly effective for AOIs >125.5°, irrespective of thrombus analog features. However, its efficacy decreased for acute AOIs. Rescue stent retriever thrombectomy was effective in 92.6% of cases of DTA failure.
Conclusions: This in vitro study confirmed that the AOI formed by the aspiration catheter and the thrombus analog influenced DTA efficacy, with an AOI >125.5° related to an effective DTA. Stent retriever thrombectomy was an effective rescue treatment after DTA failure, even in the presence of an unfavorable AOI.
Keywords: device; stent; stroke; thrombectomy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: PM is consultant for Medtronic and Stryker.
Figures
References
-
- Turk AS, Siddiqui A, Fifi JT, et al. . Aspiration thrombectomy versus stent retriever thrombectomy as first-line approach for large vessel occlusion (COMPASS): a multicentre, randomised, open label, blinded outcome, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2019;393:998–1008. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30297-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Behme D, Kowoll A, Weber W, et al. . M1 is not M1 in ischemic stroke: the disability-free survival after mechanical thrombectomy differs significantly between proximal and distal occlusions of the middle cerebral artery M1 segment. J Neurointerv Surg 2015;7:559–63. 10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011212 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
