Predicting all-cause 90-day hospital readmission for dental patients using machine learning methods
- PMID: 33483463
- PMCID: PMC7822935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41405-021-00057-6
Predicting all-cause 90-day hospital readmission for dental patients using machine learning methods
Abstract
Introduction: Hospital readmission rates are an indicator of the health care quality provided by hospitals. Applying machine learning (ML) to a hospital readmission database offers the potential to identify patients at the highest risk for readmission. However, few studies applied ML methods to predict hospital readmission. This study sought to assess ML as a tool to develop prediction models for all-cause 90-day hospital readmission for dental patients.
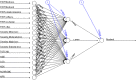
Methods: Using the 2013 Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD), the study identified 9260 cases for all-cause 90-day index admission for dental patients. Five ML classification algorithms including decision tree, logistic regression, support vector machine, k-nearest neighbors, and artificial neural network (ANN) were implemented to build predictive models. The model performance was estimated and compared by using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), and accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and precision.
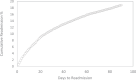
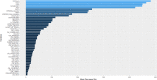
Results: Hospital readmission within 90 days occurred in 1746 cases (18.9%). Total charges, number of diagnosis, age, number of chronic conditions, length of hospital stays, number of procedures, primary expected payer, and severity of illness emerged as the top eight important features in all-cause 90-day hospital readmission. All models had similar performance with ANN (AUC = 0.743) slightly outperforming the rest.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates a potential annual saving of over $500 million if all of the 90-day readmission cases could be prevented for 21 states represented in the NRD. Among the methods used, the prediction model built by ANN exhibited the best performance. Further testing using ANN and other methods can help to assess important readmission risk factors and to target interventions to those at the greatest risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

