Utility of T2-weighted MRI texture analysis in assessment of peripheral zone prostate cancer aggressiveness: a single-arm, multicenter study
- PMID: 33483545
- PMCID: PMC7822867
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81272-x
Utility of T2-weighted MRI texture analysis in assessment of peripheral zone prostate cancer aggressiveness: a single-arm, multicenter study
Abstract
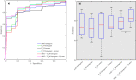
T2-weighted (T2W) MRI provides high spatial resolution and tissue-specific contrast, but it is predominantly used for qualitative evaluation of prostate anatomy and anomalies. This retrospective multicenter study evaluated the potential of T2W image-derived textural features for quantitative assessment of peripheral zone prostate cancer (PCa) aggressiveness. A standardized preoperative multiparametric MRI was performed on 87 PCa patients across 6 institutions. T2W intensity and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram, and T2W textural features were computed from tumor volumes annotated based on whole-mount histology. Spearman correlations were used to evaluate association between textural features and PCa grade groups (i.e. 1-5). Feature utility in differentiating and classifying low-(grade group 1) vs. intermediate/high-(grade group ≥ 2) aggressive cancers was evaluated using Mann-Whitney U-tests, and a support vector machine classifier employing "hold-one-institution-out" cross-validation scheme, respectively. Textural features indicating image homogeneity and disorder/complexity correlated significantly (p < 0.05) with PCa grade groups. In the intermediate/high-aggressive cancers, textural homogeneity and disorder/complexity were significantly lower and higher, respectively, compared to the low-aggressive cancers. The mean classification accuracy across the centers was highest for the combined ADC and T2W intensity-textural features (84%) compared to ADC histogram (75%), T2W histogram (72%), T2W textural (72%) features alone or T2W histogram and texture (77%), T2W and ADC histogram (79%) combined. Texture analysis of T2W images provides quantitative information or features that are associated with peripheral zone PCa aggressiveness and can augment their classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- van der Leest M, et al. Head-to-head comparison of transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy versus multiparametric prostate resonance imaging with subsequent magnetic resonance-guided biopsy in biopsy-naïve men with elevated prostate-specific antigen: a large prospective multicenter clinical study. Eur. Urol. 2019;75:570–578. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.11.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Epstein JI, Feng Z, Trock BJ, Pierorazio PM. Upgrading and downgrading of prostate cancer from biopsy to radical prostatectomy: incidence and predictive factors using the modified Gleason grading system and factoring in tertiary grades. Eur. Urol. 2012;61:1019–1024. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.01.050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 90368401/The liaison Committee between the Central Norway Regional Health Authority and the Norwegian University of Science and Technology
- 90265300/The liaison Committee between the Central Norway Regional Health Authority and the Norwegian University of Science and Technology
- 100792-2013/The Norwegian Cancer Society
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

