Artificial hibernation/life-protective state induced by thiazoline-related innate fear odors
- PMID: 33483561
- PMCID: PMC7822961
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-01629-2
Artificial hibernation/life-protective state induced by thiazoline-related innate fear odors
Abstract
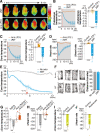
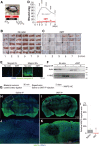
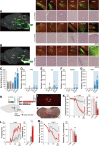
Innate fear intimately connects to the life preservation in crises, although this relationships is not fully understood. Here, we report that presentation of a supernormal innate fear inducer 2-methyl-2-thiazoline (2MT), but not learned fear stimuli, induced robust systemic hypothermia/hypometabolism and suppressed aerobic metabolism via phosphorylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase, thereby enabling long-term survival in a lethal hypoxic environment. These responses exerted potent therapeutic effects in cutaneous and cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury models. In contrast to hibernation, 2MT stimulation accelerated glucose uptake in the brain and suppressed oxygen saturation in the blood. Whole-brain mapping and chemogenetic activation revealed that the sensory representation of 2MT orchestrates physiological responses via brain stem Sp5/NST to midbrain PBN pathway. 2MT, as a supernormal stimulus of innate fear, induced exaggerated, latent life-protective effects in mice. If this system is preserved in humans, it may be utilized to give rise to a new field: "sensory medicine."
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Nedergaard J, Cannon B. Mammalian hibernation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. 1990;326:669–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

