A global perspective on the issue of access to insulin
- PMID: 33483763
- PMCID: PMC8012321
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-020-05375-2
A global perspective on the issue of access to insulin
Abstract
The discovery of insulin in 1921 changed the prognosis for people with type 1 diabetes. A century later, availability and affordability of insulin remain a challenge in many parts of the globe. Using the WHO's framework on understanding the life cycle of medicines, this review details the global and national challenges that affect patients' abilities to access and afford insulin. Current research and development in diabetes has seen some innovations, but none of these have truly been game-changing. Currently, three multinational companies control over 95% of global insulin supply. The inclusion of insulin on the WHO's Prequalification Programme is an opportunity to facilitate entry of new companies into the market. Many governments lack policies on the selection, procurement, supply, pricing and reimbursement of insulin. Moreover, mark-ups in the supply chain also affect the final price to the consumer. Whilst expenses related to diabetes are mostly covered by insurance in high-income countries, many patients from low- and middle-income countries have to pay out of their own pockets. The organisation of diabetes management within the healthcare system also affects patient access to insulin. The challenges affecting access to insulin are complex and require a wide range of solutions. Given that 2021 marks the centenary of the discovery of insulin, there is need for global advocacy to ensure that the benefits of insulin and innovations in diabetes care reach all individuals living with diabetes.
Keywords: Developing countries; Diabetes mellitus; Health services accessibility; Insulin; Review.
Figures
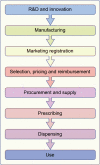

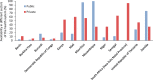
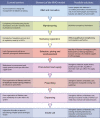
References
-
- Lawrence RD. The diabetic life. 17. London: J & A Churchill Ltd; 1965.
-
- World Health Organization . Global report on diabetes. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

