Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Thyroid Function Traits Identifies Novel Associations of fT3 With KLF9 and DOT1L
- PMID: 33484127
- PMCID: PMC8063248
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa975
Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Thyroid Function Traits Identifies Novel Associations of fT3 With KLF9 and DOT1L
Abstract
Context: Circulating concentrations of free triiodothyronine (fT3), free thyroxine (fT4), and thyrotropin (TSH) are partly heritable traits. Recent studies have advanced knowledge of their genetic architecture. Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation (DNAm), may be important in pituitary-thyroid axis regulation and action, but data are limited.
Objective: To identify novel associations between fT3, fT4, and TSH and differentially methylated positions (DMPs) in the genome in subjects from 2 Australian cohorts.
Method: We performed an epigenome-wide association study (EWAS) of thyroid function parameters and DNAm using participants from: Brisbane Systems Genetics Study (median age 14.2 years, n = 563) and the Raine Study (median age 17.0 years, n = 863). Plasma fT3, fT4, and TSH were measured by immunoassay. DNAm levels in blood were assessed using Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip arrays. Analyses employed generalized linear mixed models to test association between DNAm and thyroid function parameters. Data from the 2 cohorts were meta-analyzed.
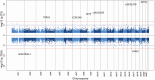
Results: We identified 2 DMPs with epigenome-wide significant (P < 2.4E-7) associations with TSH and 6 with fT3, including cg00049440 in KLF9 (P = 2.88E-10) and cg04173586 in DOT1L (P = 2.09E-16), both genes known to be induced by fT3. All DMPs had a positive association between DNAm and TSH and a negative association between DNAm and fT3. There were no DMPs significantly associated with fT4. We identified 23 differentially methylated regions associated with fT3, fT4, or TSH.
Conclusions: This study has demonstrated associations between blood-based DNAm and both fT3 and TSH. This may provide insight into mechanisms underlying thyroid hormone action and/or pituitary-thyroid axis function.
Keywords: DNA methylation; DOT1L; EWAS; KLF9; epigenetics; thyroid hormone.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Comment in
-
Toward Epigenetic Profiling of Thyroid Hormone Status.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 May 13;106(6):e2444-e2446. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab141. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33693780 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siu C, Wiseman S, Gakkhar S, et al. . Characterization of the human thyroid epigenome. J Endocrinol. 2017;235(2):153-165. - PubMed
-
- Andersen S, Pedersen KM, Bruun NH, Laurberg P. Narrow individual variations in serum T(4) and T(3) in normal subjects: a clue to the understanding of subclinical thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(3):1068-1072. - PubMed
-
- Bano A, Chaker L, Mattace-Raso FUS, et al. . Thyroid function and the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: the rotterdam study. Circ Res. 2017;121(12):1392-1400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

