Kv1.1 deficiency alters repetitive and social behaviors in mice and rescues autistic-like behaviors due to Scn2a haploinsufficiency
- PMID: 33484493
- PMCID: PMC8035482
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2041
Kv1.1 deficiency alters repetitive and social behaviors in mice and rescues autistic-like behaviors due to Scn2a haploinsufficiency
Abstract
Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and epilepsy are highly comorbid, suggesting potential overlap in genetic etiology, pathophysiology, and neurodevelopmental abnormalities; however, the nature of this relationship remains unclear. This work investigated how two ion channel mutations, one associated with autism (Scn2a-null) and one with epilepsy (Kcna1-null), interact to modify genotype-phenotype relationships in the context of autism. Previous studies have shown that Scn2a+/- ameliorates epilepsy in Kcna1-/- mice, improving survival, seizure characteristics, and brain-heart dynamics. Here, we tested the converse, whether Kcna1 deletion modifies ASD-like repetitive and social behaviors in Scn2a+/- mice.
Methods: Mice were bred with various combinations of Kcna1 and Scn2a knockout alleles. Animals were assessed for repetitive behaviors using marble burying, grooming, and nestlet shredding tests and for social behaviors using sociability and social novelty preference tests.
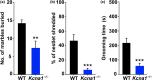
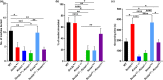
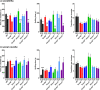
Results: Behavioral testing revealed drastic reductions in all repetitive behaviors in epileptic Kcna1-/- mice, but relatively normal social interactions. In contrast, mice with partial Kcna1 deletion (Kcna1+/- ) exhibited increased self-grooming and decreased sociability suggestive of ASD-like features similar to those observed in Scn2a+/- mice. In double-mutant Scn2a+/- ; Kcna1+/- mice, the two mutations interacted to partially normalize ASD-like behaviors associated with each mutation independently.
Conclusions: Taken together, these findings suggest that Kv1.1 subunits are important in pathways and neural networks underlying ASD and that Kcna1 may be a therapeutic target for treatment of Scn2a-associated ASD.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; channelopathies; comorbidity; epilepsy; ion channels.
© 2021 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Scn2a deletion improves survival and brain-heart dynamics in the Kcna1-null mouse model of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP).Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Jun 1;26(11):2091-2103. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx104. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28334922 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin β3 in forebrain Emx1-expressing cells regulates repetitive self-grooming and sociability in mice.BMC Neurosci. 2022 Mar 5;23(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12868-022-00691-2. BMC Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35247972 Free PMC article.
-
High-Fat Diet Exacerbates Autistic-Like Restricted Repetitive Behaviors and Social Abnormalities in CC2D1A Conditional Knockout Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;60(3):1331-1352. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03146-1. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36445635
-
Clinical Spectrum of KCNA1 Mutations: New Insights into Episodic Ataxia and Epilepsy Comorbidity.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 17;21(8):2802. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082802. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32316562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding SCN2A Variants: Bridging Genetics and Phenotypes in Autism Spectrum Disorder.J Clin Med. 2025 May 28;14(11):3790. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113790. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-Specific Behavioral Features of Juvenile and Adult Haploinsufficient Scn2a+/- Female Mice, Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder.Genes Brain Behav. 2025 Oct;24(5):e70034. doi: 10.1111/gbb.70034. Genes Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40887751 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering SCN2A: A comprehensive review of rodent models of Scn2a dysfunction.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 15:arXiv:2411.10421v1. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: Epilepsia. 2025 Aug 30. doi: 10.1111/epi.18615. PMID: 39606727 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. No abstract available.
-
Shared behavioural impairments in visual perception and place avoidance across different autism models are driven by periaqueductal grey hypoexcitability in Setd5 haploinsufficient mice.PLoS Biol. 2024 Jun 10;22(6):e3002668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002668. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38857283 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel KCNA2 Variant in a Patient with Non-Progressive Congenital Ataxia and Epilepsy: Functional Characterization and Sensitivity to 4-Aminopyridine.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 14;22(18):9913. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189913. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576077 Free PMC article.
-
Visual and auditory attention in individuals with DYRK1A and SCN2A disruptive variants.Autism Res. 2025 May;18(5):909-921. doi: 10.1002/aur.3202. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Autism Res. 2025. PMID: 39080977 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

