Effects of implant buccal distance on peri-implant strain: A Micro-CT based finite element analysis
- PMID: 33485035
- PMCID: PMC7933109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104325
Effects of implant buccal distance on peri-implant strain: A Micro-CT based finite element analysis
Abstract
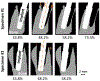
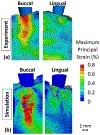
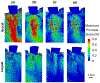
Bone-implant mechanics is one of the factors that contribute to implant stability and success. In this work, voxel-based finite element models were built based on the micro-CT images of human cadaveric mandible specimens before and after implant placement. The computed results show high strain at the bone-implant contact locations and the buccal and lingual bone plates. The strain concentration in the thinner buccal plates was more substantial than that in the thicker lingual plates. The average values of maximum principal strain in the buccal and lingual ROIs were in good agreement with those measured using mechanical testing coupled with micro-CT and digital volume correlation. The implant position was then virtually changed in the models to be placed lingually or buccally. The computed strain in the buccal bone decreased when the implant was placed away from the buccal plate. The strain in lingual bone also deceased when the implant was moved from the center of the alveolar socket towards the lingual or buccal plate. The results indicate that the distance from implant to the buccal plate can affect the mechanical stimuli in bone, especially in the buccal plate, which may subsequently affect the bone remodeling process and buccal bone resorption.
Keywords: Bone; Finite element; Implant; Mechanical strain.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

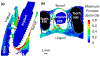
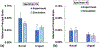
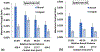
References
-
- Basaruddin KS, Takano N, Nakano T, 2015. Stochastic multi-scale prediction on the apparent elastic moduli of trabecular bone considering uncertainties of biological apatite (BAp) crystallite orientation and image-based modelling. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin 18, 162–174. 10.1080/10255842.2013.785537 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brizuela-Velasco A, Pérez-Pevida E, Jiménez-Garrudo A, Gil-Mur FJ, Manero JM, Punset-Fuste M, Chávarri-Prado D, Diéguez-Pereira M, Monticelli F, 2017. Mechanical Characterisation and Biomechanical and Biological Behaviours of Ti-Zr Binary-Alloy Dental Implants. Biomed Res. Int 2017, 1–10. 10.1155/2017/2785863 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen ST, Buser D, 2009. Clinical and esthetic outcomes of implants placed in postextraction sites. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 24 Suppl, 186–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

