Vitamin D supplementation, COVID-19 and disease severity: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 33486522
- PMCID: PMC7928587
- DOI: 10.1093/qjmed/hcab009
Vitamin D supplementation, COVID-19 and disease severity: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Current meta-analysis aims to understand the effect of oral supplementation of vitamin D on intensive care unit (ICU) requirement and mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Methods: Databases PubMed, preprint servers, and google scholar were searched from December 2019 to December 2020. Authors searched for the articles assessing role of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19. Cochrane RevMan tool was used for quantitative assessment of the data, where heterogeneity was assessed using I2 and Q statistics and data was expressed using odds ratio with 95% confidence interval.
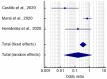
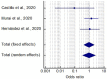
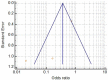
Results: Final meta-analysis involved pooled data of 532 hospitalized patients (189 on vitamin D supplementation and 343 on usual care/placebo) of COVID-19 from three studies (Two randomized controlled trials, one retrospective case-control study). Statistically (p<0.0001) lower ICU requirement was observed in patients with vitamin D supplementation as compared to patients without supplementations (odds ratio: 0.36; 95% CI: 0.210-0.626). However, it suffered from significant heterogeneity, which reduced after sensitivity analysis. In case of mortality, vitamin D supplements has comparable findings with placebo treatment/usual care (odds ratio: 0.93; 95% CI: 0.413-2.113; p=0.87). The studies did not show any publication bias and had fair quality score. Subgroup analysis could not be performed due to limited number of studies and hence dose and duration dependent effect of vitamin D could not be evaluated.
Conclusions: Although the current meta-analysis findings indicate potential role of vitamin D in improving COVID-19 severity in hospitalized patients, more robust data from randomized controlled trials are needed to substantiate its effects on mortality.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Association of Physicians. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Xiao L, Xing C, Yang Z, Xu S, Wang M, Du H, et al. Vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of childhood acute respiratory infections: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Br J Nutr 2015; 114:1026–34. - PubMed
-
- Jolliffe DA, Camargo CA, Sluyter JD, Aglipay M, Aloia JF, Ganmaa D, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials. MedRxiv 2020; doi: 10.1101/2020.07.14.20152728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical