The calcium-activated chloride channel-associated protein rCLCA2 is expressed throughout rat epidermis, facilitates apoptosis and is downmodulated by UVB
- PMID: 33486586
- PMCID: PMC8134295
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-021-01962-5
The calcium-activated chloride channel-associated protein rCLCA2 is expressed throughout rat epidermis, facilitates apoptosis and is downmodulated by UVB
Abstract
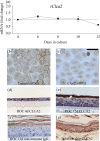
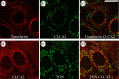
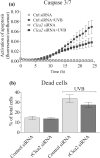
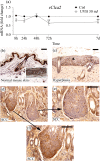
The rodent chloride channel regulatory proteins mCLCA2 and its porcine and human homologues pCLCA2 and hCLCA2 are expressed in keratinocytes but their localization and significance in the epidermis have remained elusive. hCLCA2 regulates cancer cell migration, invasion and apoptosis, and its loss predicts poor prognosis in many tumors. Here, we studied the influences of epidermal maturation and UV-irradiation (UVR) on rCLCA2 (previous rCLCA5) expression in cultured rat epidermal keratinocytes (REK) and correlated the results with mCLCA2 expression in mouse skin in vivo. Furthermore, we explored the influence of rCLCA2 silencing on UVR-induced apoptosis. rClca2 mRNA was strongly expressed in REK cells, and its level in organotypic cultures remained unchanged during the epidermal maturation process from a single cell layer to fully differentiated, stratified cultures. Immunostaining confirmed its uniform localization throughout the epidermal layers in REK cultures and in rat skin. A single dose of UVR modestly downregulated rClca2 expression in organotypic REK cultures. The immunohistochemical staining showed that CLCA2 localized in basal and spinous layers also in mouse skin, and repeated UVR induced its partial loss. Interestingly, silencing of rCLCA2 reduced the number of apoptotic cells induced by UVR, suggesting that by facilitating apoptosis, CLCA2 may protect keratinocytes against the risk of malignancy posed by UVB-induced corrupt DNA.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Epidermis; REK; UVR; rCLCA2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
rClca2 is associated with epidermal differentiation and is strongly downregulated by ultraviolet radiation.Br J Dermatol. 2014 Aug;171(2):376-87. doi: 10.1111/bjd.13038. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Br J Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24702167
-
Increased matriptase zymogen activation by UV irradiation protects keratinocyte from cell death.J Dermatol Sci. 2016 Jul;83(1):34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Dermatol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26996264
-
Synthesis of porcine pCLCA2 protein during late differentiation of keratinocytes of epidermis and hair follicle inner root sheath.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Dec;350(3):445-53. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1482-9. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22968961
-
UV-Induced Molecular Signaling Differences in Melanoma and Non-melanoma Skin Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:27-40. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-56017-5_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29124688 Review.
-
DNA damage, apoptosis and langerhans cells--Activators of UV-induced immune tolerance.Photochem Photobiol. 2008 Mar-Apr;84(2):422-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2007.00284.x. Epub 2008 Jan 29. Photochem Photobiol. 2008. PMID: 18248501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hair follicle stem cells promote epidermal regeneration under expanded condition.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 22;15:1306011. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1306011. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38455843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In focus in HCB.Histochem Cell Biol. 2021 May;155(5):525-528. doi: 10.1007/s00418-021-01991-0. Epub 2021 May 11. Histochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33977373 No abstract available.
-
Evolutionarily conserved properties of CLCA proteins 1, 3 and 4, as revealed by phylogenetic and biochemical studies in avian homologues.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 13;17(4):e0266937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266937. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35417490 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Investigations of p53 Acetylation Enabled by Heterobifunctional Molecules.ACS Chem Biol. 2024 Sep 20;19(9):1918-1929. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00438. Epub 2024 Sep 9. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39250704
-
Genomic, biochemical and expressional properties reveal strong conservation of the CLCA2 gene in birds and mammals.PeerJ. 2022 Nov 8;10:e14202. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14202. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36389428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Ghany M, Cheng HC, Elble RC, Lin H, DiBiasio J, Pauli BU. The interacting binding domains of the β(4) integrin and calcium-activated chloride channels (CLCAs) in metastasis. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:49406–49416. - PubMed
-
- Baden HP, Kubilus J. The growth and differentiation of cultured newborn rat keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1983;80:124–130. - PubMed
-
- Bart G, Hämäläinen L, Rauhala L, Salonen P, Kokkonen M, Dunlop TW, Pehkonen P, Kumlin T, Tammi MI, Pasonen-Seppänen S, Tammi RH. rClca2 is associated with epidermal differentiation and is strongly downregulated by ultraviolet radiation. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:376–387. - PubMed
-
- Beckley JR, Pauli BU, Elble RC. Re-expression of detachment-inducible chloride channel mCLCA5 suppresses growth of metastatic breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:41634–41641. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

