Proof-of-concept of a low-dose unmodified mRNA-based rabies vaccine formulated with lipid nanoparticles in human volunteers: A phase 1 trial
- PMID: 33487468
- PMCID: PMC7825876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.12.070
Proof-of-concept of a low-dose unmodified mRNA-based rabies vaccine formulated with lipid nanoparticles in human volunteers: A phase 1 trial
Abstract
Introduction: In a first-in-human study immune responses to rabies virus glycoprotein (RABV-G)-mRNA vaccine were dependent on the route of administration, necessitating specialized devices. Following successful preclinical studies with mRNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNP), we tested an mRNA-LNP formulation (CV7202).
Methods: In this phase 1, multi-center, controlled study in Belgium and Germany we enrolled 55 healthy 18-40-year-olds to receive intramuscular injections of 5 μg (n = 10), 1 μg (n = 16), or 2 μg (n = 16) CV7202 on Day 1; subsets (n = 8) of 1 μg and 2 μg groups received second doses on Day 29. Controls (n = 10) received rabies vaccine, Rabipur, on Days 1, 8 and 29. Safety and reactogenicity were assessed up to 28 days post-vaccination using diary cards; immunogenicity was measured as RABV-G-specific neutralizing titers (VNT) by RFFIT and IgG by ELISA.
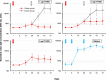
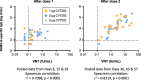
Results: As initially tested doses of 5 μg CV7202 elicited unacceptably high reactogenicity we subsequently tested 1 and 2 μg doses which were better tolerated. No vaccine-related serious adverse events or withdrawals occurred. Low, dose-dependent VNT responses were detectable from Day 15 and by Day 29%, 31% and 22% of 1, 2 and 5 μg groups, respectively, had VNTs ≥ 0·5 IU/mL, considered an adequate response by the WHO. After two 1 or 2 μg doses all recipients had titers ≥ 0.5 IU/mL by Day 43. Day 57 GMTs were not significantly lower than those with Rabipur, which elicited adequate responses in all vaccinees after two doses. CV7202-elicited VNT were significantly correlated with RABV-G-specific IgG antibodies (r2 = 0.8319, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Two 1 μg or 2 μg doses of CV7202 were well tolerated and elicited rabies neutralizing antibody responses that met WHO criteria in all recipients, but 5 μg had unacceptable reactogenicity for a prophylactic vaccine. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03713086.
Keywords: Lipid nanoparticles; Rabies; Vaccine; mRNA.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Weaver S.C., Lecuit M. Chikungunya virus and the global spread of a mosquito-borne disease. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1231–1239. - PubMed
-
- Petersen E., Wilson M.E., Touch S., McCloskey B., Mwaba P., Bates M., et al. Rapid spread of Zika virus in the Americas—implications for public health preparedness for mass gatherings at the 2016 Brazil Olympic Games. Int J Infect Dis. 2016;44:11–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

