Molecular identification, genotyping of virulence-associated genes, and pathogenicity of cellulitis-derived Escherichia coli
- PMID: 33487989
- PMCID: PMC7811558
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.2703-2712
Molecular identification, genotyping of virulence-associated genes, and pathogenicity of cellulitis-derived Escherichia coli
Abstract
Background and aim: Avian colibacillosis, which is caused by avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC), is a major bacterial disease that affects birds of all ages worldwide, causing significant economic losses. APEC manifests in several clinical forms, including cellulitis, and its high pathogenicity is attributed to harboring numerous virulence-associated genes (VGs). This study evaluated the pathogenicity of the cellulitis-derived E. coli (O78) strain through molecular identification of genes coding for seven virulence factors and by conducting an in vivo assessment of capability for cellulitis induction in broiler chickens.
Materials and methods: This study was performed using a previously isolated and identified cellulitis-derived E. coli (O78), which was screened for seven VGs using molecular detection and identification through polymerase chain reaction followed by nucleotide sequencing and phylogenetic analysis. Experimental infection by subcutaneous (SC) inoculation in broilers and its pathogenicity was confirmed in vivo by cellulitis induction. The impact of cellulitis on broiler performance was assessed.
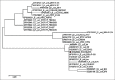
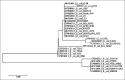
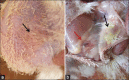
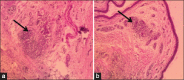
Results: Molecular genotyping proved that the isolate harbored five virulence genes (iroN, iutA, tsh, iss, and papC) and was negative for stx1 and hly genes. The amplified products for iroN, iss, and iutA were subjected to sequencing and phylogenetic analysis, and the results indicate the highest similarity and matching with E. coli submitted to the National Center for Biotechnology Information GenBank. SC inoculation of bacteria in broiler chickens resulted in cellulitis, as indicated by thick red edematous skin with yellowish-white material in the SC tissue at the inoculation site, and the abdominal muscle showed redness and increased vacuolization. Histopathological examination revealed moderate-to-severe caseous inflammatory reaction with a marked accumulation of heterophils and mononuclear cells in the SC fatty tissue. The average feed intake, body weight gain (BWG), and feed conversion ratio (FCR) were lower in infected chickens in comparison with those of the control non-infected chickens.
Conclusion: This study proves that molecular techniques are accurate for pathogenicity determination in virulent bacteria, with the advantages of being rapid, time-saving, and economical. Cellulitis is associated with economic losses that are represented by a lower BWG and FCR.
Keywords: avian pathogenic Escherichia coli; cellulitis; colibacillosis; polymerase chain reaction; virulence-associated genes.
Copyright: © Amer, et al.
Figures





References
-
- Ewers C, Janssen T, Kiessling S, Philipp H.C, Wieler L.H. Molecular epidemiology of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Molecular epidemiology of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) isolated from colisepticemia in poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2004;104(1-2):91–101. - PubMed
-
- Nolan L.K, Vaillancourt J.P, Barbieri N.L, Logue C.M. Colibacillosis. In: Swayne D.E, Boulianne M, Logue C.M, McDougald L.R, Nair V, Suarez D.L, editors. Diseases of Poultry. 14th ed. United States: Wiley-Blackwell; 2018. pp. 770–830.
-
- Johnson T.J, Wannemuehler Y, Johnson S.J, Stell A.L, Doetkott C, Johnson J.R, Kim K.S, Spanjaard L, Nolan L.K. Comparison of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli from human and avian sources reveals a mixed subset representing potential zoonotic pathogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008;74(22):7043–7050. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paixao A.C, Ferreira A.C, Fontes M, Themudo P, Albuquerque T, Soares M.C, Fevereiro M, Martins L, Correa de Sa M.I. Detection of virulence-associated genes in pathogenic and commensal avian Escherichia coli isolates. Poult. Sci. 2016;95(7):1646–1652. - PubMed
-
- Barnes H.J, Nolan L.K, Vaillancourt J.P. Colibacillosis. In: Saif Y.M, Fadly A.M, Glisson J.R, McDougald L.R, Nolan L.K, Swayne D.E, editors. Diseases of Poultry. 12th ed. United States: Blackwell Publishing; 2013. pp. 691–737.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
