Selenium Nanoparticles by Moderating Oxidative Stress Promote Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Osteoblasts
- PMID: 33488075
- PMCID: PMC7814244
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S285233
Selenium Nanoparticles by Moderating Oxidative Stress Promote Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Osteoblasts
Abstract
Purpose: Redox homeostasis plays an important role in the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) for bone engineering. Oxidative stress (OS) is believed to induce osteoporosis by changing bone homeostasis. Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs), an antioxidant with pleiotropic pharmacological activity, prevent bone loss. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the osteogenic activity during hMSC-SeNP interaction is unclear.
Methods: This study assessed the effects of different concentrations (25, 50, 100, and 300 ng/mL) of SeNPs on the cell viability and differentiation ability of human embryonic stem cell-derived hMSCs. In addition, we analyzed OS markers and their effect on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) during osteogenesis.
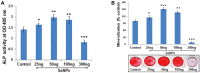
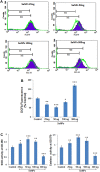
Results: SeNPs increased the cell viability of hMSCs and induced their differentiation toward an osteogenic over an adipogenic lineage by enhancing osteogenic transcription and mineralization, while inhibiting Nile red staining and adipogenic gene expression. By preventing excessive reactive oxygen species accumulation, SeNPs increased antioxidant levels in hMSCs undergoing osteogenesis compared to untreated cells. In addition, SeNPs significantly upregulated the gene and protein expression of phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and FOXO3a, with no significant change in the expression levels of extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) and p38 MAPK.
Conclusion: The results approved that low concentrations of SeNPs might enhance the cell viability and osteogenic potential of hMSCs by moderating OS. Increased JNK and FOXO3a expression shows that SeNPs might enhance osteogenesis via activation of the JNK/FOXO3 pathway. In addition, SeNP co-supplementation might prevent bone loss by enhancing osteogenesis and, thus, can be an effective candidate for treating osteoporosis through cell-based therapy.
Keywords: antioxidant; osteogenic differentiation; selenium nanoparticles stem cells.
© 2021 Fatima et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
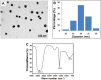
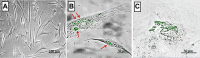
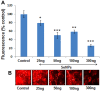
 ) agglomerates in hMSCs (Scale bar 50µm); (C) Aggregated SeNPs within the cytoplasm of the cell (Scale bar 50µm).
) agglomerates in hMSCs (Scale bar 50µm); (C) Aggregated SeNPs within the cytoplasm of the cell (Scale bar 50µm).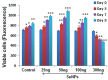


Similar articles
-
Enhancing effects of myricetin on the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via BMP-2/Smad and ERK/JNK/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 5;834:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30012495
-
Icariin induces osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells in a MAPK-dependent manner.Cell Prolif. 2015 Jun;48(3):375-84. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12185. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Cell Prolif. 2015. PMID: 25867119 Free PMC article.
-
Periostin promotes migration and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells via the Jun amino-terminal kinases (JNK) pathway under inflammatory conditions.Cell Prolif. 2017 Dec;50(6):e12369. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12369. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Cell Prolif. 2017. PMID: 28833827 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and lipid metabolism in the development of osteoporosis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Jul;54(1):61. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5385. Epub 2024 May 31. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38818830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Selenium Nanoparticles in Localized Drug Targeting for Cancer Therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022 Aug 4;22(15):2715-2725. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220215122756. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35168523 Review.
Cited by
-
Metal-based nanomaterials and nanocomposites as promising frontier in cancer chemotherapy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Apr 4;4(2):e253. doi: 10.1002/mco2.253. eCollection 2023 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37025253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium nanoparticles activate selenoproteins to mitigate septic lung injury through miR-20b-mediated RORγt/STAT3/Th17 axis inhibition and enhanced mitochondrial transfer in BMSCs.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Mar 20;23(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03312-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40114196 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances of nanomaterials for the acceleration of fracture healing.Bioact Mater. 2023 Aug 27;31:368-394. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.08.016. eCollection 2024 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 37663621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine: Where Challenge Meets Opportunity.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jul;10(20):e2207334. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207334. Epub 2023 May 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37162248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Loaded with Selenium or Nano Selenium as a Novel Therapeutic Paradigm for Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes in Rats.Biology (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;13(4):253. doi: 10.3390/biology13040253. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38666865 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

