The Biological Roles of Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancers
- PMID: 33488093
- PMCID: PMC7814250
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S281175
The Biological Roles of Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancers
Abstract
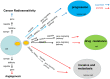
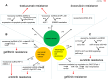
Although it has many treatment strategies, cancer is still one of the most common causes of morbidity and mortality in the world. Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles (EVs) that can be secreted by almost all cells. Exosomes can encapsulate various types of molecules, including lipids, proteins, DNA, messenger RNAs, and non-coding RNAs [microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs)]. Exosome release is a way of communication between cells. They act as powerful signaling molecules between cancer cells and the surrounding cells that make up the cancer microenvironment. lncRNAs are a class of non-coding P, with a length of more than 200 bp, which are differentially expressed in many cancers. lncRNAs have been widely regarded as a new medium for cancer behavior. The presence of lncRNAs in circulation can be acellular or encapsulated in exosomal bodies released by cancer cells. Exosomal lncRNAs are functional and can transmit different phenotypic patterns to neighboring cells. Here, we reviewed the molecular mechanism of exosomal lncRNAs in regulating cancer progression, angiogenesis, and chemotherapy resistance, as well as the prospective applications of exosomal lncRNAs in cancer diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. These findings potentially promote the current understanding of exosomal lncRNAs and provide a new research direction for exosomal lncRNAs in cancer prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Keywords: cancer; exosome; long non-coding RNAs.
© 2021 Da et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

