GC-MS analysis of the methanolic extracts of Smilax china and Salix alba and their antioxidant activity
- PMID: 33488162
- PMCID: PMC7671229
- DOI: 10.3906/kim-1907-5
GC-MS analysis of the methanolic extracts of Smilax china and Salix alba and their antioxidant activity
Abstract
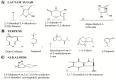
Smilax china L. (family Smilacaceae) and Salix alba L. (family Salicaceae) are plants that have been traditionally used to treat various ailments in Indian and Chinese medicine. A quantitative estimation of the methanolic extracts of these plants was performed by GC-MS analysis to obtain insight into its phytoconstituents responsible for therapeutic action. The antioxidant potential of the methanol extracts of Smilax china (MESC) and Salix alba (MESA) were assessed with DPPH by using a UV spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 517 nm. The prevailing compounds found in MESC were lactam sugars including 2,5-dimethyl-2,4-dihydroxy-3(2H)-furanon (1.40%), 1,5-anhydro-6-deoxyhexo-2,3-diulose (4.33%), and alpha-methyl-1-sorboside (1.80%); the two alkaloids found were 1,4-methane-4,4a,5,6,7,8,9,9a-octahydro-10,10-dimethyl cyclohepta[d] pyridazine (0.87%) and 1,3,7-trimethyl-2,6-dioxopurine(0.54%); terpenes included deltacadinene (0.39%), terpineol, (+)-cedrol (22.13%), 3-thujanol (0.77%), and 9,10-dehydro-cycloisolongifolene (0.34%); fatty acids included cis-vaccenic acid (4.98%) and telfairic acid (1.10%); esters included 1,2,3-propanetriol diacetate (7.56%), 7-hexadecenoic acid, methyl ester (1.77%), eicosanoic acid, and methyl ester (0.95%); and glycerol included 1,2,3-propanetriol (28.75%). The interesting compounds found in MESA were reducing sugars like D-allose (4.40%) and pyrogallol (10.48%), alkaloids like caffeine (63.49%), and esters like methyl octadecanoate (0.53%). Both fractions revealed considerable antioxidant activity. The reported existing phenolic compounds and terpenes are responsible for the antioxidant activity of the plant extracts.
Keywords: DPPH assay; GC-MS; Salix alba; Smilax china; total antioxidant potential.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization. Report of the WHO Interregional Workshop on the Use of Traditional Medicine in Primary Health Care (Ulaanbaatar . 2007.
-
- Phytochemistry of Plants Used in Traditional Medicine 1995.
-
- Kaufman PB Cseke LJ Warber S. Natural products from plants. Journal of Natural Products . 1999;62:203–203.
-
- Saravan KS Felicia C Sundarapandian SS Sathiyanaryanamurthy. Preliminary phytochemical screening of different solvent extracts of root tuber of \textit{Smilax china} International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Science Archive . 2014;7:1–5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
