From a Sociological Given Context to Changing Practice: Transforming Problematic Power Relations in Educational Organizations to Overcome Social Inequalities
- PMID: 33488472
- PMCID: PMC7817860
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.608502
From a Sociological Given Context to Changing Practice: Transforming Problematic Power Relations in Educational Organizations to Overcome Social Inequalities
Abstract
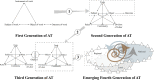
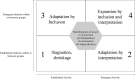
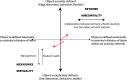
In 2012, the international PISA survey reinforced the observation that the French educational system is one of the most unequal among OECD countries. The observation of serious inequalities in access to educational success for pupils from disadvantaged backgrounds could lead to a pessimistic vision suggesting that any possibility of transformation of the system is doomed to failure. Thus, the fight against inequalities in access to educational success is a form of runaway object which constitutes a challenge for research which treats the social context as evolving and susceptible to significant and novel transformations. Developmental work research aims to support the work of professionals in the re-elaboration of their practices by seeking to go beyond the status quo of an unequal school. Drawing on this framework within an institutional network of schools, we seek to show how the intervention has highlighted power issues inscribed in the structures and how the actors, through their commitment in the research collaborative process, seek to go beyond the power issues inscribed in their work routines and enacted during the research process by different kinds of antagonism. We will argue that the fight against educational inequality involves overcoming systemic power relations crystallized in institution. This systemic power is expressed by a form of episodic power. Our results show restrictive and constructive effect on the expansive learning process and on the construction of a collective in the formative interventions. The restrictive side of epistemic power should be linked to systemic power which is historically inherited. We discuss the results in the light of the emergence of a fourth generation of activity theory. Our research makes it possible to make conceptual and methodological progress in the construction of a fourth generation of activity theory by showing the need for analysis and expansively learn about problematic power relations in heterogeneous collectives.
Keywords: Cultural-historical activity theory (CHAT); development; inequalities; interventionist research; power relations.
Copyright © 2021 Lémonie, Grosstephan and Tomás.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bardon T., Josserand E. (2018). Management innovations from a foucauldian perspective: Time to take action. [Management innovations from a foucauldian perspective: time to take action]. M@n@gement 21 1244–1263. 10.3917/mana.214.1244 - DOI
-
- Blacker F. (2009). “Cultural-Historical ctivity Theory and Organization Studies,” in Learning and Expanding with Activity Theory, eds Sannino A., Daniels H., Gutierrez K. D. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; ), 19–39.
-
- Blacker F., McDonald S. (2000). Power, mastery and organizational learning. J. Manag. Stud. 37 833–852. 10.1111/1467-6486.00206 - DOI
-
- Bourdieu P., Passeron J.-C. (1970). La reproduction. Élèments Pour une Théorie du Système D’enseignement. Paris: Éditions de minuit.
-
- Bronfenbrenner U. (1977). Toward an experimental ecology of human development. Am. Psychol. 32 513–531. 10.1037/0003-066X.32.7.513 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

