Prevalence and Risk Factors of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients With Hyperthyroidism
- PMID: 33488520
- PMCID: PMC7821907
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.605712
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients With Hyperthyroidism
Abstract
Background: Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction has been demonstrated to be an independent predictor of the future heart failure. Heart failure is one of the severe complications caused by overt hyperthyroidism. However, the effects of overt hyperthyroidism on diastolic dysfunction are conflicting, and little is known about the prevalence and risk factors of the diastolic dysfunction in patients with overt hyperthyroidism.
Methods: A total of 388 patients with overt hyperthyroidism were included and compared with 388 age- and gender- matched euthyroid control subjects. LV diastolic function was evaluated by traditional and tissue-Doppler echocardiography. Routine clinical medical data and echocardiographic parameters were recorded for analysis.
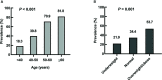
Results: The prevalence of LV diastolic dysfunction was 35.1% among hyperthyroid patients and significantly higher than control subjects whose prevalence was 25.5% (P = 0.003), and it increased with age and body mass index (BMI) in patients with overt hyperthyroidism. The possible risk factors for LV diastolic dysfunction, such as hypertension, diabetes, decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and increased level of thyroid hormones weren't associated with LV diastolic dysfunction. However, overweight or obese were significantly associated with LV diastolic dysfunction (OR = 3.024, 95% CI = 1.517-6.027, P = 0.002) compared with normal BMI. When compared with age <40 years old group, 40-50 years old group, 50-60 years old group and age ≥60 years old group were significantly associated with LV diastolic dysfunction, with ORs of 2.976 (95% CI = 1.744-5.019), 12.424 (95% CI = 4.934-31.283), 24.966 (95% CI = 5.975-104.321), respectively.
Conclusion: LV diastolic dysfunction was very common, in particular, in older and overweight or obese patients with overt hyperthyroidism. Additionally, age and BMI were independent risk factors for LV diastolic dysfunction, while the level of thyroid hormones was not. Therefore, besides the LV systolic function, we also need focus on the diastolic function in patients with overt hyperthyroidism in clinical work, especially the older and overweight or obese patients.
Keywords: echocardiography; hyperthyroidism; left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; prevalence; risk factors.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Zeng, Liao, Fu, Zhang, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous