C4b Binding Protein Acts as an Innate Immune Effector Against Influenza A Virus
- PMID: 33488586
- PMCID: PMC7820937
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.585361
C4b Binding Protein Acts as an Innate Immune Effector Against Influenza A Virus
Abstract
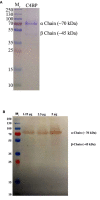
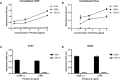
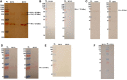
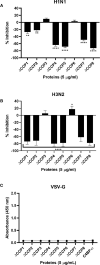
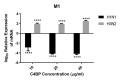
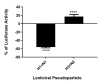
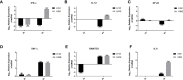
C4b Binding Protein (C4BP) is a major fluid phase inhibitor of the classical and lectin pathways of the complement system. Complement inhibition is achieved by binding to and restricting the role of activated complement component C4b. C4BP functions as a co-factor for factor I in proteolytic inactivation of both soluble and cell surface-bound C4b, thus restricting the formation of the C3-convertase, C4b2a. C4BP also accelerates the natural decay/dissociation of the C3 convertase. This makes C4BP a prime target for exploitation by pathogens to escape complement attack, as seen in Streptococcus pyogenes or Flavivirus. Here, we examined whether C4BP can act on its own in a complement independent manner, against pathogens. C4BP bound H1N1 and H3N2 subtypes of Influenza A Virus (IAV) most likely via multiple sites in Complement Control Protein (CCP) 1-2, 4-5, and 7-8 domains of its α-chain. In addition, C4BP CCP1-2 bound H3N2 better than H1N1. C4BP bound three IAV envelope proteins: Haemagglutinin (~70 kDa), Neuraminidase (~55 kDa), and Matrix protein 1 (~25kDa). C4BP suppressed H1N1 subtype infection into the lung epithelial cell line, A549, while it promoted infection by H3N2 subtype. C4BP restricted viral entry for H1N1 but had the opposite effect on H3N2, as evident from experiments using pseudo-typed viral particles. C4BP downregulated mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory IFN-α, IL-12, and NFκB in the case of H1N1, while it promoted a pro-inflammatory immune response by upregulating IFN- α, TNF-α, RANTES, and IL-6 in the case of H3N2. We conclude that C4BP differentially modulates the efficacy of IAV entry, and hence, replication in a target cell in a strain-dependent manner, and acts as an entry inhibitor for H1N1. Thus, CCP containing complement proteins such as factor H and C4BP may have additional defense roles against IAV that do not rely on the regulation of complement activation.
Keywords: C4BP; complement; inflammation; influenza A virus; pseudo-typed lentiviral particles.
Copyright © 2021 Varghese, Murugaiah, Beirag, Temperton, Khan, Alrokayan, Al-Ahdal, Nal, Al-Mohanna, Sim and Kishore.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer KR declared a shared affiliation with one of the authors, RS, to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
References
-
- Okrój M, Blom AM. The complement facts book. London, United Kingdom:Academic Press; (2018). 10.1016/c2015-0-06595-9 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

