PCSK9 genetic variants and cognitive abilities: a large-scale Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 33488877
- PMCID: PMC7811317
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms/127226
PCSK9 genetic variants and cognitive abilities: a large-scale Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Introduction: PCSK9 inhibitors lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and are efficacious at reducing vascular disease, however questions remain about potential effects on cognitive function.
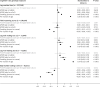
Methods: We examined the association of genetic variants in PCSK9 with continuous measures of cognitive ability in UK Biobank. Six independent polymorphisms in PCSK9 were used in up to 337,348 individuals.
Results: The PCSK9 allele score was associated with a lower risk of CHD, and weakly with worse log reaction time.
Conclusions: We are unable to rule out meaningful associations of PCSK9 genetic variants with cognition, emphasising the potential need for continued pharmacovigilance for patients currently treated with PCSK9 inhibitors.
Keywords: cardiovascular genomics; epidemiology; low-density lipoprotein.
Copyright: © 2021 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The Clinical Trial Service Unit and Epidemiological Studies Unit at the University of Oxford (MVH) has received research grants from Abbott/Solvay/Mylan, AstraZeneca, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Schering. MVH has collaborated with Boehringer Ingelheim in research, and in accordance with the policy of the Clinical Trial Service Unit and Epidemiological Studies Unit (University of Oxford), did not accept any personal payment. NS has consulted for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Sanofi, and Boehringer Ingelheim. All other authors have nothing to report.
Figures
References
-
- Collins R, Reith C, Emberson J, et al. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet. 2016;388:2532–61. - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, Blazing MA, Giugliano RP, et al. Ezetimibe added to statin therapy after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2387–97. - PubMed
-
- Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Keech AC, et al. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1713–22. - PubMed
-
- Swiger KJ, Martin SS. PCSK9 inhibitors and neurocognitive adverse events: exploring the FDA directive and a proposal for N-of-1 trials. Drug Saf. 2015;38:519–26. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous