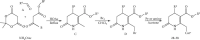Pleiotropic Properties of Amphiphilic Dihydropyridines, Dihydropyridones, and Aminovinylcarbonyl Compounds
- PMID: 33488932
- PMCID: PMC7790557
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8413713
Pleiotropic Properties of Amphiphilic Dihydropyridines, Dihydropyridones, and Aminovinylcarbonyl Compounds
Abstract
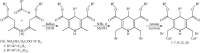
Three groups of synthetic lipids are chosen for studies: (1) 1,4-dihydropyridines (1,4-DHPs) containing two cationic moieties and their analogues; (2) 3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-pyridones containing a cationic moiety; and (3) acyclic, open-chain analogues, i.e., 2-amino-3-alkoxycarbonylalkylammonium derivatives. 1,4-DHPs possessing dodecyl alkyl chains in the ester groups in positions 3 and 5 and cationic nitrogen-containing groups in positions 2 and 6 have high cytotoxicity in cancer cells HT-1080 (human lung fibrosarcoma) and MH-22A (mouse hepatoma), but low cytotoxicity in the noncancerous NIH3T3 cells (mouse embryonic fibroblast). On the contrary, similar compounds having short (methyl, ethyl, or propoxyethyl) chains in the ester groups in positions 3 and 5 lack cytotoxicity in the cancer cells HT-1080 and MH-22A even at high doses. Inclusion of fluorine atoms in the alkyl chains in positions 3 and 5 of the DHP cycle decreases the cytotoxicity of the mentioned compounds. Structurally related dihydropyridones with a polar head group are substantially more toxic to normal and cancerous cells than the DHP analogues. Open-chain analogues of DHP lipids comprise the same conjugated aminovinylcarbonyl moiety and possess anticancer activity, but they also have high basal cytotoxicity. Electrochemical oxidation data demonstrate that oxidation potentials of selected compounds are in the range of 1.6-1.7 V for cationic 1,4-DHP, 2.0-2.4 V for cationic 3,4-dihydropyridones, and 1.2-1.5 V for 2-amino-3-alkoxycarbonylalkylammonium derivatives. Furthermore, the tested cationic 1,4-DHP amphiphiles possess antiradical activity. Molecular topological polar surface area values for the tested compounds were defined in accordance with the main fragments of compound structures. The determined logP values were highest for dodecyl ester groups in positions 3 and 5 of the 1,4-DHP and lowest for short alkyl chain-containing amphiphiles.
Copyright © 2020 Martins Rucins et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical