HSP60 Regulates Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Inflammation by Activating the TLR4-NF- κ B-MyD88 Signaling Pathway and Disrupting Mitochondrial Function
- PMID: 33488933
- PMCID: PMC7791970
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8706898
HSP60 Regulates Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Inflammation by Activating the TLR4-NF- κ B-MyD88 Signaling Pathway and Disrupting Mitochondrial Function
Abstract
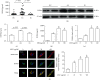
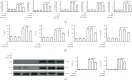
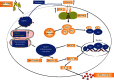
Acute gout is an inflammatory response induced by monosodium urate (MSU) crystals. HSP60 is a highly conserved stress protein that acts as a cellular "danger" signal for immune reactions. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role and molecular mechanism of HSP60 in gout. HSP60 expression was detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and plasma of gout patients. The effect and molecular mechanism of HSP60 in gout were studied in MSU crystals treatment macrophages and C57BL/6 mice. JC-1 probe and MitoSOX Red were used to measure the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS). HSP60 expression was significantly upregulated in the PBMCs and sera of patients with acute gout (AG) compared to those with intercritical gout (IG) or healthy controls (HCs). MSU crystals induced the expression and secretion of HSP60 in the macrophages. HSP60 knockdown or overexpression affects TLR4 and MyD88 expression, IκBα degradation, and the nuclear localization of NF-κB in MSU crystal-stimulated inflammation. Further, HSP60 facilitates MMP collapse and mtROS production and activates the NLRP3 inflammasome in MSU crystal-stimulated macrophages. In MSU crystal-induced arthritis mouse models pretreated with HSP60 vivo-morpholino, paw swelling, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, and inflammatory cell infiltration significantly decreased. Our study reveals that MSU crystal stimulates the expression of HSP60, which accelerates the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway and exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction.
Copyright © 2020 Qiushi Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Curcumin attenuates MSU crystal-induced inflammation by inhibiting the degradation of IκBα and blocking mitochondrial damage.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Aug 27;21(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1974-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31455356 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Berberine on Activation of TLR4-NFκB Signaling Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Patients with Gout.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Jan;29(1):10-18. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3720-7. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36125615
-
HSP60 regulates the cigarette smoke-induced activation of TLR4-NF-κB-MyD88 signalling pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Feb;103:108445. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108445. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34998273
-
The Role of Inhibitory Receptors in Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 20;9:1883. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01883. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30177932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of crystal induced inflammation: current understandings and clinical implications.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Jul;17(7):773-787. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1937129. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34053376 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Baicalin on Gout Based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and in vitro Experiments.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 4;18:1543-1556. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S480911. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39925939 Free PMC article.
-
TAK-242 improves sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in rats by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2313176. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2313176. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38482886 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinase USP16 induces gouty arthritis via Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Jul 24;25(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03095-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37488647 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Response to Regulated Cell Death in Gout and Its Functional Implications.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 6;13:888306. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.888306. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35464445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in the design of functional derivatives of edaravone and exploration of their antioxidant activities.Mol Divers. 2025 Apr;29(2):1895-1910. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10940-7. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39102113 Review.
References
-
- Chen‐Xu M., Yokose C., Rai S. K., Pillinger M. H., Choi H. K. Contemporary prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the United States and decadal trends: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007-2016. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2019;71(6):991–999. doi: 10.1002/art.40807. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

