Pharmacological Modulation of Cardiac Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 33488934
- PMCID: PMC7790555
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8815349
Pharmacological Modulation of Cardiac Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
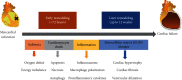
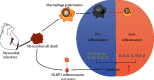
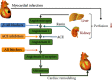
Cardiac remodeling describes a series of structural and functional changes in the heart after myocardial infarction (MI). Adverse post-MI cardiac remodeling directly jeopardizes the recovery of cardiac functions and the survival rate in MI patients. Several classes of drugs are proven to be useful to reduce the mortality of MI patients. However, it is an ongoing challenge to prevent the adverse effects of cardiac remodeling. The present review aims to identify the pharmacological therapies from the existing clinical drugs for the treatment of adverse post-MI cardiac remodeling. Post-MI cardiac remodeling is a complex process involving ischemia/reperfusion, inflammation, cell death, and deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Thus, the present review included two parts: (1) to examine the basic pathophysiology in the cardiovascular system and the molecular basis of cardiac remodeling and (2) to identify the pathological aspects of cardiac remodeling and the potential of the existing pharmacotherapies. Ultimately, the present review highlights drug repositioning as a strategy to discover effective therapies from the existing drugs against post-MI cardiac remodeling.
Copyright © 2020 Wei Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

