Neuroprotection Effect of Astragaloside IV from 2-DG-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
- PMID: 33488941
- PMCID: PMC7790552
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9782062
Neuroprotection Effect of Astragaloside IV from 2-DG-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Abstract
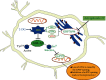
Objective: Astragaloside IV shows neuroprotective activity, but its mechanism remains unclear. To investigate whether astragaloside IV protects from endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), we focus on the regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) by astragaloside IV in neuronal cell PC12.
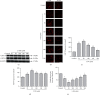
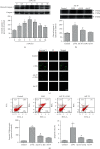
Methods and results: PC12 cells treated with different concentrations of ERS inductor 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) (25-500 μM) showed a significant increase of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP 78) and GRP 94 expressions and a decrease of tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester (TMRE) fluorescence intensity and mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ψm), with the peak effect seen at 50 μM, indicating that 2-DG induces ERS and the mPTP opening. Similarly, 50 μM of astragaloside IV increased the GSK-3β phosphorylation at Ser9 most significantly. Next, we examined the neuroprotection of astragaloside IV by dividing the PC12 cells into control group, 2-DG treatment group, astragaloside IV plus 2-DG treatment group, and astragaloside IV only group. PC12 cells treated with 50 μM 2-DG for different time courses (0-36 hr) showed a significant increase of Cleaved-Caspase-3 with the peak at 6 hr. 2-DG significantly induced cell apoptosis and increased the green fluorescence intensity of Annexin V-FITC, and these effects were reversed by astragaloside IV. Such a result indicates that astragaloside IV protected neural cell survival from ERS. 2-DG treatment significantly increased the expressions of inositol-requiring ER-to-nucleus signal kinase 1 (IRE1), phosphor-protein kinase R-like ER kinase (p-PERK), but not affect the transcription factor 6 (ATF6) expression. 2-DG treatment significantly decreased the phosphorylation of GSK-3β and significantly reduced the TMRE fluorescence intensity and ∆Ψm, following mPTP open. Astragaloside IV significantly inhibited the above effects caused by 2-DG, except the upregulation of ATF6 protein. Taken together, astragaloside IV significantly inhibited the ERS caused by 2-DG.
Conclusion: Our data suggested that astragaloside IV protects PC12 cells from ERS by inactivation of GSK-3β and preventing the mPTP opening. The GRP 78, GRP 94, IRE1, and PERK signaling pathways but not ATF6 are responsible for GSK-3β inactivation and neuroprotection by astragaloside IV.
Copyright © 2020 Yu Fu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

