Machine learning applications in drug development
- PMID: 33489002
- PMCID: PMC7790737
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.12.006
Machine learning applications in drug development
Abstract
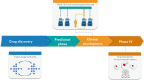
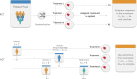
Due to the huge amount of biological and medical data available today, along with well-established machine learning algorithms, the design of largely automated drug development pipelines can now be envisioned. These pipelines may guide, or speed up, drug discovery; provide a better understanding of diseases and associated biological phenomena; help planning preclinical wet-lab experiments, and even future clinical trials. This automation of the drug development process might be key to the current issue of low productivity rate that pharmaceutical companies currently face. In this survey, we will particularly focus on two classes of methods: sequential learning and recommender systems, which are active biomedical fields of research.
Keywords: Adaptive clinical trial; Bayesian optimization; Collaborative filtering; Drug discovery; Drug repurposing; Multi-armed bandit.
© 2019 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Eliopoulos H., Giranda V., Carr R., Tiehen R., Leahy T., Gordon G. Phase 0 trials: an industry perspective. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(12):3683–3688. - PubMed
-
- Khanna I. Drug discovery in pharmaceutical industry: productivity challenges and trends. Drug Discovery Today. 2012;17(19–20):1088–1102. - PubMed
-
- Hwang T.J., Carpenter D., Lauffenburger J.C., Wang B., Franklin J.M., Kesselheim A.S. Failure of investigational drugs in late-stage clinical development and publication of trial results. JAMA Internal Med. 2016;176(12):1826–1833. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
