Hypoglycemic activity of the ethyl acetate extract from Smilax glabra Roxb in mice: Biochemical and histopathological studies
- PMID: 33489029
- PMCID: PMC7811822
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.46658.10763
Hypoglycemic activity of the ethyl acetate extract from Smilax glabra Roxb in mice: Biochemical and histopathological studies
Abstract
Objectives: This research was carried out to investigate the hypoglycemic activity of the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract from the roots of Smilax glabra Roxb, which strongly exhibit inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase and α-amylase on in vivo type 2 diabetic model.
Materials and methods: Column chromatography combined with crystallization was used to isolate the active fraction and compounds. Chemical structures of the compounds were determined based on the analysis of the spectroscopic data and comparison with the literature data. The α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (AGI) and the α-amylase inhibitory activity (AAI) were determined quantitatively spectrophotometrically using p-nitrophenyl α-D-glucopyranoside and soluble starch as substrates, respectively. The hypoglycemic activity was examined by evaluating its effects on glucose and insulin levels, insulin resistance, and histopathology of the pancreatic islets and livers in diabetic induced mice administrated with nicotinamide-streptozotocin.
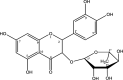
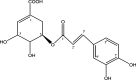
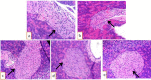
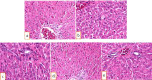
Results: The EtOAc extract and the bioactive compounds astilbin and 5-O-caffeoylshikimic acid in the extract were isolated and confirmed in structures, AGI, and AAI. The treatment at the doses of 500 and 1000 µg/kg of body weight reduced blood glucose levels down to the physiological level of the physical controls in the diabetic mice after two weeks (P<0.05). Moreover, the treatment improved insulin sensitivity. Histopathology analysis showed recovering effects in the size of the pancreatic islets and no damaging effects on the liver after treatment compared with the control group.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that the EtOAc extract possesses hypoglycemic activity and has an antidiabetic potential for therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Alpha-amylase; Alpha-glucosidase; Diabetes; Ethyl acetate (EtOAc) – extract; In vivo model; Smilax glabra Roxb.
Figures

References
-
- Ahamad J, Naquvi K, Mir RS, Ali M, Shuaib M. Review on role of natural alpha-glucosidase inhibitors for management of diabetes mellitus. IJBR. 2011;2:374–380.
-
- Kalra S. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. J Pak Med Assoc. 2014;64:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Kang W. Alpha glucosidase inhibitory in vitro and antidiabetic activity in vivo of Osmanthus fragrans. J Med Plants Res. 2012;6:2850–2856.
-
- Nishibori N, Sawaguchi M, Hiroi T. Inhibitory effects of aqueous extract prepared from joint part of lotus root on alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase activities. Phytopharmacology. 2012;3:1–11.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
