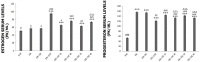Effects of soy isoflavonoids (genistein and daidzein) on endometrial receptivity
- PMID: 33489035
- PMCID: PMC7811811
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.48294.11089
Effects of soy isoflavonoids (genistein and daidzein) on endometrial receptivity
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to examine the effects of genistein and daidzein on endometrial receptivity by histopathological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical techniques.
Materials and methods: In this study, 72 female Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into 8 groups. The endometrial receptivity model was applied to identified groups. Experimental animals were given periorally 10 mg/kg and high 40 mg/kg doses of genistein and daidzein for 5 days by gavage. At the end of the experiment, uterine tissues were evaluated histopathologically, immunohistochemically, and biochemically.
Results: When histopathological findings were examined, significant decreases in pinopod formation were observed in high dose genistein and daidzein groups. When compared with the endometrial receptivity group, immunohistochemical staining findings showed a significant decrease in the expression of integrin β3, integrin αvβ3, LIF, and HOXA10 and an increase in MUC 1 expression in the high dose of genistein and daidzein groups. In biochemical evaluations, it was determined that genistein and daidzein increased estrogen levels and decreased progesterone levels in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Genistein and daidzein have a negative effect on endometrial receptivity. Therefore, individuals with a risk of infertility should pay attention to the consumption of genistein and daidzein.
Keywords: Daidzein; Endometrial Receptivity; Genistein; Rat; Soy Isoflavonoids.
Figures
References
-
- Dilara Nilüfer DB. Soya ve Soya Ürünlerinin Fonksiyonel Gıda Bileşenleri. Dergipark. 2008;33:241–250.
-
- Dalu A, Haskell JF, Coward L, Lamartiniere CA. Genistein, a component of soy, inhibits the expression of the EGF and ErbB2/Neu receptors in the rat dorsolateral prostate. Prostate. 1998;37:36–43. - PubMed
-
- Wei HC, Bowen R, Cai QY, Barnes S, Wang Y. Anti-oxidant and antipromotional effects of the soybean isoflavone genistein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1995;208:124–130. - PubMed
-
- Kar PK, Tandon V, Saha NN. Anthelmintic efficacy of genistein, the active principle of Flemingia vestita (Fabaceae): Alterations in the free amino acid pool and ammonia levels in the fluke, Fasciolopsis buski. Parasitol Int. 2004;53:287–291. - PubMed
-
- Cooke PS, Selvaraj V, Yellayi S. Genistein, estrogen receptors, and the acquired immune response. J Nutr. 2006;136:704–708. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials