Beneficial Effects of Amnion-Chorion Stem Cell Grafting in the Long Term Management of Nonuremic Calciphylaxis Wounds
- PMID: 33489581
- PMCID: PMC7813429
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12170
Beneficial Effects of Amnion-Chorion Stem Cell Grafting in the Long Term Management of Nonuremic Calciphylaxis Wounds
Abstract
Calciphylaxis is a poorly understood disease with high morbidity and mortality. The current primary literature on treatment is lacking; however, disease management often involves a multifaceted approach with a primary focus on consistent wound care. This report describes a case outlining the long-term management of nonuremic calciphylaxis wounds in a patient with severe malnutrition with the use of human amniotic membrane grafts, aggressive surgical debridement, nutritional therapy, and advanced wound healing techniques. A 38-year-old African American female with a history of non-uremic calciphylaxis presented from a transitional facility with numerous non-healing wounds in the setting of severe malnutrition secondary to bariatric surgery. Biweekly wound debridement was initiated utilizing an amniotic stem cell skin graft, dry applicable absorbent dressing, high-frequency ultrasonic ablation, and wound vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) over the course of approximately nine months. Nutritional supplementation was given in the form of jejunostomy tube feed due to a gastric bypass and a perforated viscus. At the current date, the patient demonstrates significant improvement in pain and wound healing. The patient is also able to ambulate with care and has begun steps towards independent management of wounds. Future goals of care include independent bedside wound management, placement of allograft, and discharge to a long-term care facility. Most patients with refractory pain, widespread necrotic wounds, and dangerous comorbidities will inevitably be referred to palliative care. This case creates a framework for the long term management of medically complex patients with nonuremic calciphylaxis using human amniotic membrane stem cell grafts and appropriate advanced wound care techniques.
Keywords: advanced wound care; amnionic stem cell graft; non uremic calciphylaxis; wound debridement.
Copyright © 2020, Bhamidipati et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
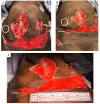
Figures


References
-
- Calciphylaxis is usually non-ulcerating: risk factors, outcome and therapy. Fine A, Zacharias J. Kidney Int. 2002;61:2210–2217. - PubMed
-
- Survival, risk factors, and effect of treatment in 101 patients with calciphylaxis. McCarthy JT, El-Azhary RA, Patzelt MT, et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:1384–1394. - PubMed
-
- Calciphylaxis in patients on hemodialysis: a prevalence study. Angelis M, Wong LL, Myers SA, Wong LM. Surgery. 1997;122:1083–1090. - PubMed
-
- Calciphylaxis. Nigwekar SU, Thadhani R, Brandenburg VM. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1704–1714. - PubMed
-
- Nonuremic calciphylaxis triggered by rapid weight loss and hypotension. Kolb LJ, Ellis C, Lafond A. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32074157/ Cutis. 2020;105:11. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
