The Metabolic Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis
- PMID: 33489906
- PMCID: PMC7817624
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.602416
The Metabolic Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis
Abstract
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancy among women worldwide. Metastasis is mainly responsible for treatment failure and is the cause of most breast cancer deaths. The role of metabolism in the progression and metastasis of breast cancer is gradually being emphasized. However, the regulatory mechanisms that conduce to cancer metastasis by metabolic reprogramming in breast cancer have not been expounded. Breast cancer cells exhibit different metabolic phenotypes depending on their molecular subtypes and metastatic sites. Both intrinsic factors, such as MYC amplification, PIK3CA, and TP53 mutations, and extrinsic factors, such as hypoxia, oxidative stress, and acidosis, contribute to different metabolic reprogramming phenotypes in metastatic breast cancers. Understanding the metabolic mechanisms underlying breast cancer metastasis will provide important clues to develop novel therapeutic approaches for treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; glycolysis; hypoxia; metabolic phenotypes; metabolism; metastasis; molecular mechanisms.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
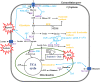
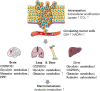
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

