Regulation of Hedgehog Signaling by miRNAs and Nanoformulations: A Possible Therapeutic Solution for Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 33489917
- PMCID: PMC7817854
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.607607
Regulation of Hedgehog Signaling by miRNAs and Nanoformulations: A Possible Therapeutic Solution for Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
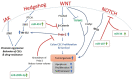
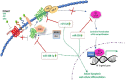
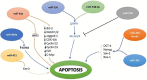
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling aberrations trigger differentiation and proliferation in colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the current approaches which inhibit this vital cellular pathway provoke some side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to look for new therapeutic options. MicroRNAs are small molecules that modulate expression of the target genes and can be utilized as a potential therapeutic option for CRC. On the other hand, nanoformulations have been implemented in the treatment of plethora of diseases. Owing to their excessive bioavailability, limited cytotoxicity and high specificity, nanoparticles may be considered as an alternative drug delivery platform for the Hh signaling mediated CRC. This article reviews the Hh signaling and its involvement in CRC with focus on miRNAs, nanoformulations as potential diagnostic/prognostic and therapeutics for CRC.
Keywords: Hedgehog signaling; colorectal cancer; miRNAs; nanoformulations; nanoparticle; therapeutics.
Copyright © 2021 Javed, Javed Iqbal, Rasheed, Sadia, Raza, Irshad, Koch, Kukula-Koch, Głowniak-Lipa, Cho and Sharifi-Rad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

