The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on Patients Undergoing Primary Total Lower Extremity Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33490250
- PMCID: PMC7787736
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6661691
The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on Patients Undergoing Primary Total Lower Extremity Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a common disease that has an adverse impact on most orthopedic surgeries, and its prevalence has gradually increased in recent years. We aim to investigate the influence of DM on comorbidities and complications of patients undergoing primary total lower extremity arthroplasty.
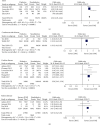
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Medline, and Web of Science were systematically searched for relevant studies published before December 2019. Demographic data, comorbidities, and postoperative complications after primary total hip arthroplasties (THA) or primary total knee arthroplasties (TKA) were assessed between DM and non-DM patients. Meta-analysis was conducted using Review Manager 5.3, and forest plots were drawn for each variable.
Results: A total of 1,560,461 patients (215,916 patients with DM and 1,344,545 patients without DM) from 23 studies were included in this meta-analysis. The incidences of several preoperative comorbidities (hypertension (HTN), kidney disease, cardiac and cerebrovascular disease) were generally higher in patients with DM. Moreover, DM patients had a higher rate of postoperative complications (superficial and deep infection, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and in-hospital mortality) compared to non-DM patients.
Conclusions: DM patients were more likely to suffer from comorbidities and had a higher risk of complications in total lower extremity arthroplasty compared to non-DM patients. It is necessary to identify DM and control hyperglycemia in the perioperative period to prevent postoperative complications in patients with DM.
Copyright © 2020 Wanjin Qin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Impact of preoperative anemia on patients undergoing total joint replacement of lower extremity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Apr 18;19(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04706-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38637795 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative hyperglycemia and postoperative infection after lower limb arthroplasty.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011 Mar 1;5(2):412-8. doi: 10.1177/193229681100500231. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011. PMID: 21527113 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin dependence increases the risk of postoperative complications and inferior outcome but not the survivorship of total joint arthroplasty among diabetic population: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022 May;32(4):701-709. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-03027-8. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34097155
-
Effect of Type 2 Diabetes on In-Hospital Postoperative Complications and Mortality After Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2017 Dec;32(12):3729-3734.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.06.038. Epub 2017 Jul 5. J Arthroplasty. 2017. PMID: 28735804
-
Comorbidities and perioperative complications in HIV-positive patients undergoing primary total hip and knee arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Jun 5;95(11):1028-36. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.L.00269. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013. PMID: 23780541
Cited by
-
Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on Postoperative Complications After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Oct 26;60(11):1757. doi: 10.3390/medicina60111757. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39596942 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative strategies to prevent periprosthetic joint infection after knee replacement: evidence-based recommendations for multidisciplinary practice.Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2025 Aug 29;17:143566. doi: 10.52965/001c.143566. eCollection 2025. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2025. PMID: 40894246 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Risk of Infection in Patients with Diabetes following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 120,754 Knees.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 28;11(13):3752. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133752. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35807033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of diabetes on the risk of deep vein thrombosis of patients after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Mar 4;19(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04624-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38439085 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of a Methylprednisolone Taper and Complication Rates Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Multicenter Retrospective Study.Arthroplast Today. 2025 Mar 8;32:101603. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2024.101603. eCollection 2025 Apr. Arthroplast Today. 2025. PMID: 40123731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurtz S., Ong K., Lau E., Mowat F., Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2007;89(4):780–785. - PubMed
-
- Memtsoudis S. G., Della Valle A. G., Besculides M. C., Gaber L., Laskin R. Trends in demographics, comorbidity profiles, in-hospital complications and mortality associated with primary knee arthroplasty. The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2009;24(4):518–527. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2008.01.307. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bolognesi M. P., Marchant M. H., Jr., Viens N. A., Cook C., Pietrobon R., Vail T. P. The impact of diabetes on perioperative patient outcomes after total hip and total knee arthroplasty in the United States. The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2008;23(6):92–98. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2008.05.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

