The complete mitochondrial genome of the Basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus cornucopiae (Paulet) Rolland
- PMID: 33490488
- PMCID: PMC7800982
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2017.1422405
The complete mitochondrial genome of the Basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus cornucopiae (Paulet) Rolland
Abstract
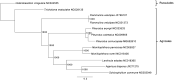
Pleurotus cornucopiae is a commercial edible and medicinal fungus. Herein, we determined and analyzed its complete mitochondrial genome. The mitogenome length was 72,134 bp with a GC content of 26.7%, contained 14 conserved protein coding genes, two rRNA genes (rnl and rns), ribosomal protein gene rps3 and 24 tRNA genes. Pleurotus cornucopiae has a similar gene content and gene order of the mitogenome as P. ostreatus and P. eryngii. A phylogenetic analysis based on complete mitogenome in related fungi showed that P. cornucopiae is a member of the order Agaricales, forming a clade with P. ostreatus and P. eryngii, with P. ostreatus as a sister taxa. The mitochondrial genome sequence of P. cornucopiae appeared a promising tool for further studies of the taxonomy and evolution of Pleurotaceae and Agaricales.
Keywords: Fungi; Pleurotus cornucopiae; evolution; mitogenome; mushroom.
© 2018 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adebayo EA, Oloke JKJ, Azeez MA, Ayandele AA, Majolagbe ON.. 2016. Compatibility study using hybridization procedure among Pleurotus genotypes and authentication by enzyme expression and ITSR of rDNA. Russian Agric Sci. 42:423–430.
-
- Chaudhary MM, John P.. 2017. Morphological and molecular characterization of oyster mushroom (Pleurotus cystidiosus). Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 6:246–250.
-
- Gao S, Huang CY, Chen Q, Bian YB, Zhang JX.. 2008. Phylogenetic relationship of Pleurotus species based on nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. J Plant Genet Resour. 9:328–334.
-
- Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O.. 2010. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol. 59:307–321. - PubMed
-
- He XL, Wu B, Li Q, Peng WH, Huang ZQ, Gan BC.. 2016. Phylogenetic relationship of two popular edible Pleurotus in China, Bailinggu (P. eryngii var. tuoliensis) and Xingbaogu (P. eryngii), determined by ITS, RPB2 and EF1α sequences. Mol Biol Rep. 43:573–582. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous