Extracellular RNAs as potential biomarkers for cancer
- PMID: 33490601
- PMCID: PMC7821910
- DOI: 10.20517/2394-4722.2020.71
Extracellular RNAs as potential biomarkers for cancer
Abstract
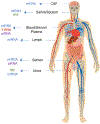
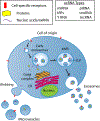
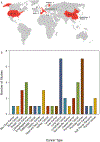
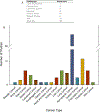
The discovery that all cells secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs) to shuttle proteins and nucleic acids to recipient cells suggested they play an important role in intercellular communication. EVs are widely distributed in many body fluids, including blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine and saliva. Exosomes are nano-sized EVs of endosomal origin that regulate many pathophysiological processes including immune responses, inflammation, tumour growth, and infection. Healthy individuals release exosomes with a cargo of different RNA, DNA, and protein contents into the circulation, which can be measured non-invasively as biomarkers of healthy and diseased states. Cancer-derived exosomes carry a unique set of DNA, RNA, protein and lipid reflecting the stage of tumour progression, and may serve as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for various cancers. However, many gaps in knowledge and technical challenges in EVs and extracellular RNA (exRNA) biology, such as mechanisms of EV biogenesis and uptake, exRNA cargo selection, and exRNA detection remain. The NIH Common Fund-supported exRNA Communication Consortium was launched in 2013 to address major scientific challenges in this field. This review focuses on scientific highlights in biomarker discovery of exosome-based exRNA in cancer and its possible clinical application as cancer biomarkers.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; biomarker; cancer; exosomes; extracellular RNA; liquid biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular RNA communication: A decade of NIH common fund support illuminates exRNA biology.J Extracell Vesicles. 2025 Jan;14(1):e70016. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70016. J Extracell Vesicles. 2025. PMID: 39815775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium: Establishing Foundational Knowledge and Technologies for Extracellular RNA Research.Cell. 2019 Apr 4;177(2):231-242. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.023. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30951667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary Extracellular Vesicle-Associated exRNA as Cancer Biomarker.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 26;11(7):891. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070891. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31247906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: Therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jun;174:63-78. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.020. Epub 2017 Feb 12. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28202367 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles (EVs)' journey in recipient cells: from recognition to cargo release.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024 Aug 15;25(8):633-655. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300566. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024. PMID: 39155778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicle RNA Contents as Biomarkers for Ocular Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1415:81-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-27681-1_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37440018
-
A deep learning method to integrate extracelluar miRNA with mRNA for cancer studies.Bioinformatics. 2024 Nov 1;40(11):btae653. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae653. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39495117 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA Metabolism and Lung Cancer: Beyond Translation.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 30;8:659388. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.659388. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34660690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Molecular Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Staging of NAFLD.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 2;22(21):11905. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111905. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular RNA communication: A decade of NIH common fund support illuminates exRNA biology.J Extracell Vesicles. 2025 Jan;14(1):e70016. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70016. J Extracell Vesicles. 2025. PMID: 39815775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 2007;9:654–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
