Melatonin attenuated the behavioral despair induced by acute neurogenic stress through blockade of N-methyl D-aspartate receptors in mice
- PMID: 33490672
- PMCID: PMC7810776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e05900
Melatonin attenuated the behavioral despair induced by acute neurogenic stress through blockade of N-methyl D-aspartate receptors in mice
Abstract
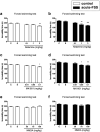
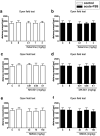
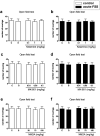
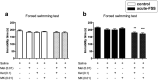
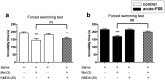
It has been well documented that administration of melatonin could reveal antidepressant-like effect in rodents. However, the protective effect of melatonin on stress-induced depression/anxiety and its underlying mechanism is yet to be understood. In this regard, in the current study, acute foot-shock stress (FSS) was used to evaluate the antidepressant-like effect of melatonin on neurogenic stress-induced depression in mice. Behavioral evaluation was done by using the forced swimming test (FST) and Open-field test (OFT). Melatonin, MK-801, and ketamine (NMDA receptor antagonists), and NMDA (NMDA receptor agonist) were used to elucidate any association between melatonin and NMDA pathway in behavioral despair induced by acute-FSS. Applying acute-FSS to mice significantly induced depressant-like behavior in FST without any significant impact on locomotor activity in the OFT. We observed that melatonin (dose-dependently) significantly improved the depressant-like effect of FSS, but it did not impact the locomotion in animals. Acute injection of MK-801 at sub-effective doses (0.01 mg/kg) or ketamine (0.1 mg/kg) potentiated the antidepressant-like effect of a sub-effective dose of melatonin. However, the sub-effective dose of NMDA (30 mg/kg) abolished the protective effect of melatonin on the behavioral profile of stressed animals. Our results could reflect the antidepressant-like effect of melatonin on neurogenic stress-induced depressive behaviors in mice. Also, our results showed that NMDA receptors could be involved in the antidepressant-like effect of melatonin.
Keywords: Acute foot shock stress; Behavioral despair; Melatonin; Mice; NMDA receptor.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Anisman H., Hayley S., Kelly O., Borowski T., Merali Z. Psychogenic, neurogenic, and systemic stressor effects on plasma corticosterone and behavior: mouse strain-dependent outcomes. Behav. Neurosci. 2001;115:443. - PubMed
-
- Berman R.M., Cappiello A., Anand A., Oren D.A., Heninger G.R., Charney D.S. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol. Psychiatr. 2000;47:351–354. - PubMed
-
- Chamanara M., Rashidian A., Mehr S.E., Dehpour A.R., Shirkohi R., Akbarian R., Abdollahi A., Rezayat S.M. Melatonin ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats through the melatonin receptors: involvement of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2019 Apr 1;27(2):361–371. - PubMed
-
- Cryan J.F., Holmes A. The ascent of mouse: advances in modelling human depression and anxiety. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:775–790. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

