Intranasal drug delivery: opportunities and toxicologic challenges during drug development
- PMID: 33491126
- PMCID: PMC7829061
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-020-00891-5
Intranasal drug delivery: opportunities and toxicologic challenges during drug development
Abstract
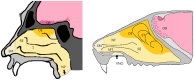
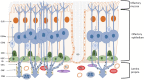
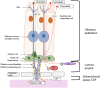
Over the past 10 years, the interest in intranasal drug delivery in pharmaceutical R&D has increased. This review article summarises information on intranasal administration for local and systemic delivery, as well as for CNS indications. Nasal delivery offers many advantages over standard systemic delivery systems, such as its non-invasive character, a fast onset of action and in many cases reduced side effects due to a more targeted delivery. There are still formulation limitations and toxicological aspects to be optimised. Intranasal drug delivery in the field of drug development is an interesting delivery route for the treatment of neurological disorders. Systemic approaches often fail to efficiently supply the CNS with drugs. This review paper describes the anatomical, histological and physiological basis and summarises currently approved drugs for administration via intranasal delivery. Further, the review focuses on toxicological considerations of intranasally applied compounds and discusses formulation aspects that need to be considered for drug development.
Keywords: Intranasal drug delivery; Nasal toxicity; Nose-to-brain-delivery; Olfactory pathways.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AbbVie sponsored and funded the study; contributed to the design; participated in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, and in writing, reviewing, and approval of the final publication. Lea-Andriana Keller and Andreas Popp are employees of AbbVie and may own AbbVie Stock. Olivia Merkel is a Professor at the Ludwig-Maximilians-University and Lea-Adriana Keller’s doctoral adviser.
Figures

References
-
- Frey W H.III. Neurologic agents for nasal administration to the brain [Internet]. 1991. Available from: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO1991007947&tab...
-
- Axel R. Scents and sensibility: a molecular logic of olfactory perception (Nobel lecture) Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44:6110–6127. - PubMed
-
- Crisler R, Johnston NA, Sivula C, Budelsky CL. Functional anatomy and physiology. Lab Rat [Internet]. Elsevier; 2020 [cited 2020 Jul 13]. p. 91–132. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780128143384000040
-
- Mygind N, Dahl R. Anatomy, physiology and function of the nasal cavities in health and disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1998;29:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Harkema JR, Carey SA, Wagner JG. The nose revisited: a brief review of the comparative structure, function, and toxicologic pathology of the nasal epithelium. Toxicol Pathol. 2006;34:252–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

