The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines as Intermediates in the Pathway from Increased Adiposity to Disease
- PMID: 33491305
- PMCID: PMC8614117
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.23060
The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines as Intermediates in the Pathway from Increased Adiposity to Disease
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the role of cytokines as intermediates in the pathway from increased adiposity to disease.
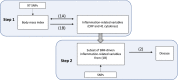
Methods: BMI and circulating levels of up to 41 cytokines were measured in individuals from three Finnish cohort studies (n = 8,293). Mendelian randomization (MR) was used to assess the impact of BMI on circulating cytokines and the impact of BMI-driven cytokines on risk of obesity-related diseases.
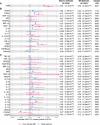
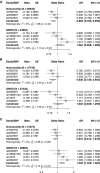
Results: Observationally, BMI was associated with 19 cytokines. For every SD increase in BMI, causal effect estimates were strongest for hepatocyte growth factor, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and were as ratios of geometric means 1.13 (95% CI: 1.08-1.19), 1.08 (95% CI: 1.04-1.14), and 1.13 (95% CI: 1.04-1.21), respectively. TRAIL was associated with a small increase in the odds of coronary artery disease (odds ratio: 1.03; 95% CI: 1.00-1.06). There was inconsistent evidence for a protective role of MCP-1 against inflammatory bowel diseases.
Conclusions: Observational and MR estimates of the effect of BMI on cytokine levels were generally concordant. There was little evidence for an effect of raised levels of BMI-driven cytokines on disease. These findings illustrate the challenges of MR when applied in the context of molecular mediation.
© 2021 The Authors. Obesity published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Obesity Society (TOS).
Conflict of interest statement
VS has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Sanofi and has received honoraria from these companies. He also has ongoing research collaboration with Bayer Ltd (all unrelated to the present study). The other authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Esser N, Legrand‐Poels S, Piette J, Scheen AJ, Paquot N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014;105:141‐150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

