Effect of Aerobic Exercise Intensity on Energy Expenditure and Weight Loss in Severe Obesity-A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33491314
- PMCID: PMC7898283
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.23078
Effect of Aerobic Exercise Intensity on Energy Expenditure and Weight Loss in Severe Obesity-A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare the effects of two aerobic exercise programs of different intensities on energy expenditure.
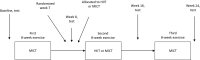
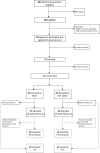
Methods: This was a single-center randomized controlled trial of patients with severe obesity allocated to a 24-week moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) program or a combined MICT with high-intensity interval training (HIIT/MICT) program. The primary outcome was energy expenditure during exercise (EEDE). Secondary outcomes included resting metabolic rate, cardiorespiratory fitness, and body composition.
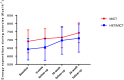
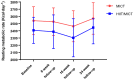
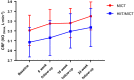
Results: A total of 82 (56% females) patients were screened, and 71 (55% females) patients were allocated to HIIT/MICT (n = 37) or MICT (n = 34). Per-protocol analysis showed that EEDE increased by 10% (95% CI: 3%-17%) in the HIIT/MICT group (n = 16) and 7.5% (95% CI: 4%-10%) in the MICT group (n = 24), with no differences between groups. In the 8- to 16- week per-protocol analysis, the HIIT/MICT group had a significantly larger increase in EEDE compared with the MICT group. Resting metabolic rate remained unchanged in both groups. HIIT/MICT and MICT were associated with significant weight loss of 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively.
Conclusions: Patients completing a 24-week combined HIIT/MICT program did not achieve a higher EEDE compared with those who completed a 24-week MICT program. The HIIT/MICT group experienced, on average, a 3-kg-larger weight loss than the MICT group.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02311738.
© 2021 The Authors. Obesity published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Obesity Society (TOS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Berge J, Storen O, Hertel JK, Gjevestad E, Smastuen MC, Hjelmesaeth J. Associations between cardiorespiratory fitness and weight loss in patients with severe obesity undergoing an intensive lifestyle intervention program: retrospective cohort study. BMC Endocr Disord 2019;19:69. doi:10.1186/s12902-019-0394-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Souza SA, Faintuch J, Sant'anna AF. Effect of weight loss on aerobic capacity in patients with severe obesity before and after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 2010;20:871‐875. - PubMed
-
- Kantartzis K, Thamer C, Peter A, et al. High cardiorespiratory fitness is an independent predictor of the reduction in liver fat during a lifestyle intervention in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2009;58:1281‐1288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

