Targeted Genetic Changes in Candida albicans Using Transient CRISPR-Cas9 Expression
- PMID: 33491919
- PMCID: PMC7842826
- DOI: 10.1002/cpz1.19
Targeted Genetic Changes in Candida albicans Using Transient CRISPR-Cas9 Expression
Erratum in
-
Group Correction Statement (Data Availability Statements).Curr Protoc. 2022 Aug;2(8):e552. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.552. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36005902 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Group Correction Statement (Conflict of Interest Statements).Curr Protoc. 2022 Aug;2(8):e551. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.551. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36005903 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correction: Targeted Genetic Changes in Candida albicans Using Transient CRISPR-Cas9 Expression.Curr Protoc. 2023 Mar;3(3):e715. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.715. Curr Protoc. 2023. PMID: 36892302 No abstract available.
Abstract
Candida albicans is an opportunistic fungal pathogen responsible for significant disease and mortality. Absent complete mating and other convenient methods, dissection of its virulence factors relies on robust tools to delete, complement, and otherwise modify genes of interest in this diploid organism. Here we describe the design principles and use of CRISPR associated nuclease 9 (Cas9) and single-guide RNAs transiently expressed from PCR cassettes to modify genes of interest, generating homozygous mutants in a single transformation step. © 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: PCR amplification of CRISPR components Basic Protocol 2: Transformation of Candida albicans Basic Protocol 3: Selecting and genotyping transformants Alternate Protocol 1: Deletion with recyclable markers by CRISPR induced marker excision (CRIME) Alternate Protocol 2: Knock-in and combining multiple cassettes with overlapping homology.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; Candida albicans; gene deletion; gene editing; transient CRISPR-Cas9 expression.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
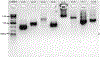

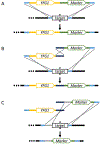
References
-
- Glazier VE, Murante T, Koselny K, Murante D, Esqueda M, Wall GA, … Krysan DJ (2018). Systematic Complex Haploinsufficiency-Based Genetic Analysis of Candida albicans Transcription Factors: Tools and Applications to Virulence-Associated Phenotypes. G3 (Bethesda, Md.), 8(4), 1299–1314. 10.1534/g3.117.300515 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

