The Estimated Lifetime Medical Cost of Syphilis in the United States
- PMID: 33492088
- PMCID: PMC10028531
- DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001353
The Estimated Lifetime Medical Cost of Syphilis in the United States
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to estimate the cost of syphilis in the United States, in terms of the average lifetime direct medical cost per infection.
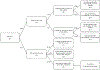
Methods: We used a decision tree model of the natural history of syphilis. The model allowed for numerous possible outcomes of infection, including treatment for syphilis at various stages, inadvertent treatment, and late syphilis outcomes in those who are alive and still infected 30 years after acquisition. Future costs were discounted at 3% annually. Model inputs, such as the cost and probability of each outcome, were based on published sources. The probabilities we applied yielded outcomes consistent with reported cases of syphilis by stage from national surveillance data and number of deaths due to late syphilis from national mortality data.
Results: The estimated, discounted lifetime cost per infection was $1190 under base case assumptions (2019 dollars). Treatment costs associated with late syphilis outcomes, such as cardiovascular syphilis, accounted for only $26 of the average lifetime cost per infection. Results were most sensitive to assumptions regarding the treatment cost per case of unknown duration or late syphilis. In the probabilistic sensitivity analyses, the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles of the 10,000 simulations of the lifetime cost per infection were $729 and $1884, respectively.
Conclusions: Our estimate of the lifetime cost per infection is about 50% higher than in a previous study, a difference due in large part to our higher cost assumptions for benzathine penicillin G.
Copyright © 2021 American Sexually Transmitted Diseases Association. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest and Sources of Funding: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Owusu-Edusei K Jr., Chesson HW, Gift TL, et al. The estimated direct medical cost of selected sexually transmitted infections in the United States, 2008. Sex Transm Dis 2013;40(3):197–201. - PubMed
-
- Chesson HW, Blandford JM, Gift TL, Tao G, Irwin KL. The estimated direct medical cost of sexually transmitted diseases among American youth, 2000. Perspect Sex Reprod Health 2004;36(1):11–19. - PubMed
-
- American Social Health Association. Sexually transmitted diseases in America: How many cases and at what cost? Menlo Park, CA: Kaiser Family Foundation;1998.
-
- Chesson HW, Rein D, Kassler WJ, et al. Direct medical costs of syphilis in the United States: The potential for a cost-saving national elimination program Poster presentation. 1998 National STD Prevention Conference; Dallas, December 6–9, 1998.
-
- Schmid GP, Zaidi A. Serologic screening for syphilis: a decision model Eleventh Meeting of the International Society for STD Research; New Orleans, August 27–30, 1995.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

