R-COMP versus R-CHOP as first-line therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients ≥60 years: Results of a randomized phase 2 study from the Spanish GELTAMO group
- PMID: 33492774
- PMCID: PMC7926012
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3730
R-COMP versus R-CHOP as first-line therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients ≥60 years: Results of a randomized phase 2 study from the Spanish GELTAMO group
Abstract
The use of non-pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Myocet® ) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) has been investigated in retrospective and single-arm prospective studies. This was a prospective phase 2 trial of DLBCL patients ≥60 years old with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥55% randomized to standard R-CHOP or investigational R-COMP (with Myocet® instead of conventional doxorubicin). The primary end point was to evaluate the differences in subclinical cardiotoxicity, defined as decrease in LVEF to <55% at the end of treatment. Secondary objectives were efficacy, safety, and variations of troponin and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and LVEF along follow-up. Ninety patients were included, 45 in each group. No differences were observed in the percentage of patients with LVEF <55% at end of treatment (11% in R-CHOP arm vs. 7% in R-COMP arm, p = 0.697) or at 4 months (10% vs. 6%, respectively, p = 0.667) and 12 months (8% vs. 7%, respectively, p = 1). However, a higher percentage of R-CHOP compared with R-COMP patients showed increased troponin levels in cycle 6 (100% vs. 63%, p = 0.001) and at 1 month after treatment (88% vs. 56%, respectively, p = 0.015). Cardiovascular adverse events were seen in five R-CHOP patients (nine episodes, four grade ≥3) and in four R-COMP patients (five episodes, all grade 1-2). No significant differences in efficacy were observed. In conclusion, R-COMP is a feasible immunochemotherapy schedule for DLBCL patients ≥60 years, with similar efficacy to R-CHOP. However, the use of non-pegylated doxorubicin instead of conventional doxorubicin was not associated with less early cardiotoxicity, although some reduced cardiac safety signals were observed. Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02012088.
Keywords: N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; cardiotoxicity; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; liposomal doxorubicin; troponin.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
JMS has received honoraria from Roche, Gilead, Janssen, Celgene, Servier, Novartis, Mundipharma, Sanofi, Kern‐Pharma, and Takeda, and was a Member of the Board of Directors or advisory committees for Roche, Janssen, Gilead, Celgene, Novartis, Bristol Myers, and Celltrion. NG has received honoraria from Roche and Janssen. EG has participated in advisory committees for Abbvie, Janssen, and Gilead. JAHR received honoraria and research funding from Roche, Janssen, Celgene, and Gilead. JMGDC received honoraria from Novartis and Alexion y Pfizer.
Figures
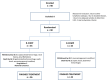


References
-
- Batist G, Ramakrishnan G, Rao CS, et al. Reduced cardiotoxicity and preserved antitumor efficacy of liposome‐encapsulated doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide compared with conventional doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide in a randomized, multicenter trial of metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:1444‐1454. - PubMed
-
- Limat S, Demesmay K, Voillat L, et al. Early cardiotoxicity of the CHOP regimen in aggressive non‐Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:277‐281. - PubMed
-
- Cardinale D, Sandri MT, Colombo A, et al. Prognostic value of troponin I in cardiac risk stratification of cancer patients undergoing high‐dose chemotherapy. Circulation. 2004;109:2749‐2754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

