Feasibility of Fitness Tracker Usage to Assess Activity Level and Toxicities in Patients With Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 33492994
- PMCID: PMC8189607
- DOI: 10.1200/CCI.20.00117
Feasibility of Fitness Tracker Usage to Assess Activity Level and Toxicities in Patients With Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Performance status (PS) is a subjective assessment of patients' overall health. Quantification of physical activity using a wearable tracker (Fitbit Charge [FC]) may provide an objective measure of patient's overall PS and treatment tolerance.
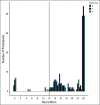
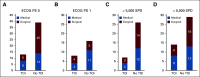
Materials and methods: Patients with colorectal cancer were prospectively enrolled into two cohorts (medical and surgical) and asked to wear FC for 4 days at baseline (start of new chemotherapy [± 4 weeks] or prior to curative resection) and follow-up (4 weeks [± 2 weeks] after initial assessment in medical and postoperative discharge in surgical cohort). Primary end point was feasibility, defined as 75% of patients wearing FC for at least 12 hours/d, 3 of 4 assigned days. Mean steps per day (SPD) were correlated with toxicities of interest (postoperative complication or ≥ grade 3 toxicity). A cutoff of 5,000 SPD was selected to compare outcomes.
Results: Eighty patients were accrued over 3 years with 55% males and a median age of 59.5 years. Feasibility end point was met with 68 patients (85%) wearing FC more than predefined duration and majority (91%) finding its use acceptable. The mean SPD count for patients with PS 0 was 6,313, and for those with PS 1, it was 2,925 (122 and 54 active minutes, respectively) (P = .0003). Occurrence of toxicity of interest was lower among patients with SPD > 5,000 (7 of 33, 21%) compared with those with SPD < 5,000 (14 of 43, 32%), although not significant (P = .31).
Conclusion: Assessment of physical activity with FC is feasible in patients with colorectal cancer and well-accepted. SPD may serve as an adjunct to PS assessment and a possible tool to help predict toxicities, regardless of type of therapy. Future studies incorporating FC can standardize patient assessment and help identify vulnerable population.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, et al. : Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:145-164, 2020 - PubMed
-
- Willett CG: Management of locoregional rectal cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 16:617-619, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Aapro M, Scotte F, Bouillet T, et al. : A practical approach to fatigue management in colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 16:275-285, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

