Asthma in Adult Patients with COVID-19. Prevalence and Risk of Severe Disease
- PMID: 33493416
- PMCID: PMC8017581
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202008-3266OC
Asthma in Adult Patients with COVID-19. Prevalence and Risk of Severe Disease
Abstract
Rationale: Health outcomes of people with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) range from no symptoms to severe illness and death. Asthma, a common chronic lung disease, has been considered likely to increase the severity of COVID-19, although data addressing this hypothesis have been scarce until very recently.Objectives: To review the epidemiologic literature related to asthma's potential role in COVID-19 severity.Methods: Studies were identified through the PubMed (MEDLINE) and medRxiv (preprint) databases using the search terms "asthma," "SARS-CoV-2" (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2), and "COVID-19," and by cross-referencing citations in identified studies that were available in print or online before December 22, 2020.Measurements and Main Results: Asthma prevalence data were obtained from studies of people with COVID-19 and regional health statistics. We identified 150 studies worldwide that allowed us to compare the prevalence of asthma in patients with COVID-19 by region, disease severity, and mortality. The results of our analyses do not provide clear evidence of increased risk of COVID-19 diagnosis, hospitalization, severity, or mortality due to asthma.Conclusions: These findings could provide some reassurance to people with asthma regarding its potential to increase their risk of severe morbidity from COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; asthma; disease severity; mortality.
Figures
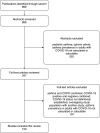
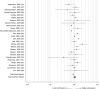
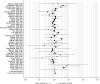
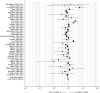
Comment in
-
Asthma and COVID-19: Preconceptions about Predisposition.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Apr 1;203(7):799-801. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202102-0266ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33600744 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO COVID-19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) global research and innovation forum Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2020[accessed 2020 Oct 29]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-public-health-emergency-of-inte...)-global-research-and-innovation-forum
-
- WHO WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) dashboard Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2020[updated 2021 Feb 2; accessed 2020 Oct 29]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int
-
- Weill Cornell Medicine COVID-19: why is it mild for some, deadly for others? New York, New York: Weill Cornell Medicine; 2020[accessed 2020 Oct 29]. Available from: https://weillcornell.org/news/COVID-19-why-is-it-mild-for-some-deadly-fo...
-
- Global Asthma Network The global asthma report Auckland, New Zealand: Global Asthma Network; 2018[accessed 2020 Oct 29]. Available from: http://www.globalasthmareport.org/Global%20Asthma%20Report%202018.pdf
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

