Mechanisms of thrombosis and cardiovascular complications in COVID-19
- PMID: 33493983
- PMCID: PMC7813504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2021.01.005
Mechanisms of thrombosis and cardiovascular complications in COVID-19
Abstract
Background: The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, responsible for the 2019-2020 global (COVID-19) pandemic, is a respiratory virus associated with the development of thromboembolic complications and respiratory failure in severe cases. Increased risk of pulmonary embolism and thrombosis has been identified in COVID-19 patients, alongside accompanying elevations in potential prognostic biomarkers, including D-dimer, IL-6 and cardiac specific troponins. Our aim was to provide a scoping review of the available literature regarding thrombosis risk, other cardiovascular implications, and their biomarkers in COVID-19 to highlight potential disease mechanisms.
Methods: Authors conducted a literature search in PubMed using MeSH headings "disseminated intravascular coagulation", "pulmonary embolism", "thromb*", "stroke", "myocardial infarction" and "acute lung injury", as well as terms "COVID-19", "SARS-CoV-2", "2019 novel coronavirus" and "2019-nCoV".
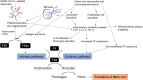
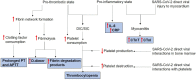
Results and conclusions: COVID-19 disease is characterised by the interactions between hyperactive coagulation and complement systems - induced by hyper-inflammatory conditions, resulting in a pro-thrombotic state and diffuse tissue injury. There are several promising prognostic markers of disease severity, with D-dimer the most significant. The presence of thrombocytopenia appears to be a key indicator of patient deterioration. Further research is required to understand the underlying pathophysiology in COVID-19 and its implications in disease progression and patient management. Randomised trials are urgently needed to determine the safety of proposed therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin and the role for anti-platelet agents, such as Ticagrelor, in patient management.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cardiovascular complications; D-dimer; SARS-CoV-2; Thromboembolism.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Atri D., Siddiqi H.K., Lang J., Nauffal V., Morrow D.A., Bohula E.A. COVID-19 for the cardiologist: a current review of the virology, clinical epidemiology, cardiac and other clinical manifestations and potential therapeutic strategies. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020;5:518–536. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2020.04.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klok F.A., Kruip M.J.H.A., van der Meer N.J.M., Arbous M.S., Gommers D.A.M.P.J., Kant K.M., Kaptein F.H.J., van Paassen J., Stals M.A.M., Huisman M.V., Endeman H. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020;191:145–147. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Middeldorp S., Coppens M., van Haaps T.F., Foppen M., Vlaar A.P., Müller M.C.A., Bouman C.C.S., Beenen L.F.M., Kootte R.S., Heijmans J., Smits L.P., Bonta P.I., van Es N. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020;18:1995–2002. doi: 10.1111/jth.14888. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

