Model-Based Prediction to Evaluate Residence Time of Hyaluronic Acid Based Dermal Fillers
- PMID: 33494145
- PMCID: PMC7909806
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020133
Model-Based Prediction to Evaluate Residence Time of Hyaluronic Acid Based Dermal Fillers
Abstract
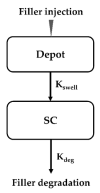
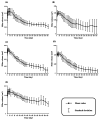
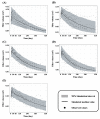
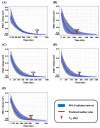
Dermal fillers are gel-type substances for nonsurgical medical-device use to achieve facial rejuvenation. Currently, the most widely used skin fillers are hyaluronic-acid-based dermal fillers. This study aimed to explain the change in the volume of injected dermal fillers by developing a mathematical kinetic model for various dermal fillers. The kinetics of the injected fillers were separated by a biphasic phenomenon. We attributed an increase in filler volume to the hydration of hyaluronic acid molecules and injection-site reaction and a decrease in volume to enzyme-mediated degradation. To explain these in vivo characteristics of dermal fillers, we proposed a two-compartment model, divided into a depot compartment (where the filler was injected) and a subcutaneous compartment (an observation compartment where the fillers swell and degrade), assuming that the swelling and degradation occurred in accordance with the swelling and degradation rate constants, respectively. The model was developed using five hyaluronic-acid-based dermal fillers and NONMEM. We determined that the rate-limiting step for the complete degradation of the dermal fillers in vivo was the swelling phase, as described by the swelling rate constant (Kswell). This study could enable scientists developing novel dermal fillers to predict the in vivo behavior of fillers.
Keywords: HA-based dermal filler; NONMEM; degradation; kinetic model; prediction; swelling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. H.-j.R., S.-s.K., C.-h.R., G.-h.Y. and W.-h.K. are the employees of Medytox Inc. The company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The science of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers.J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2008 Mar;10(1):35-42. doi: 10.1080/14764170701774901. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2008. PMID: 18330796 Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Hyaluronidase-Mediated Degradation Among Seven Hyaluronic Acid Fillers in Hairless Mice.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021 Mar 8;14:241-248. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S300960. eCollection 2021. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33727845 Free PMC article.
-
A composite dermal filler comprising cross-linked hyaluronic acid and human collagen for tissue reconstruction.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Mar;25(3):399-406. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1411.11029. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25502824
-
In Vivo Degradation of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Fillers by Exogenous Hyaluronidases.Dermatol Surg. 2018 Aug;44(8):1075-1083. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001525. Dermatol Surg. 2018. PMID: 29659410
-
The Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Current Understanding of the Tissue Device Interface.Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2015 Nov;23(4):423-32. doi: 10.1016/j.fsc.2015.07.002. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26505539 Review.
Cited by
-
New Directions in Aesthetic Medicine: A Novel and Hybrid Filler Based on Hyaluronic Acid and Lactose Modified Chitosan.Gels. 2022 May 23;8(5):326. doi: 10.3390/gels8050326. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35621624 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous and induced degradation of dermal fillers: A review.J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2024 Oct-Dec;17(4):273-281. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_137_23. Epub 2023 Nov 30. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2024. PMID: 39649762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis in Human 3D Skin Model Injected with Resorbable Hyaluronic Acid Fillers Reveals Foreign Body Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13046. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113046. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361846 Free PMC article.
-
Objective Noninvasive Measurement of the Volumizing Effect of a Dermal Filler: An In Vivo Study.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(19):4024-4030. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04138-3. Epub 2024 May 28. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38806832 Free PMC article.
-
Strengthening the Key Features of Volumizing Fillers: Projection Capacity and Long-Term Persistence.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 4;15(11):2585. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112585. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haney B. Aesthetic Procedures: Nurse Practitioner’s Guide to Cosmetic Dermatology. 1st ed. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 139–189. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

